Cervical Node Cancer: Insights and Implications
Intro
Cervical node cancer, though less discussed compared to other cancers, poses significant challenges in oncology. Affecting the lymph nodes in the neck area, its implications stretch far beyond physical health, resonating through social and emotional avenues as well. Understanding this condition is crucial for both the medical community and those affected by it. This article seeks to bring together a thorough exploration of cervical node cancer, highlighting the key points from its origins to its treatment and support mechanisms available.
Article Overview
Purpose of the Article
The primary aim of this article is to enrich the understanding of cervical node cancer. By delving into its etiology, the clinical manifestations it presents, and the available diagnostic technologies, we strive to provide a clear pathway through this daunting landscape. The intention is to facilitate early detection and intervention, which are vital for improving patient outcomes. Additionally, we will illuminate the distressing psychological and social implications that accompany a cervical node cancer diagnosis, fostering a holistic perspective on patient care.
Relevance to Multiple Disciplines
Cervical node cancer touches various fields beyond oncology. The implications reach into areas such as psychology, nursing, and health education. Each discipline plays a role in patient education and emotional support. For instance, healthcare providers require a deep understanding of both the medical and psychosocial challenges that patients face. In this way, by presenting comprehensive insights, the article serves not only those directly involved in cancer treatment but also educators and researchers who are shaping future healthcare approaches.
Research Background
Historical Context
Historically, the understanding of cervical node cancer has evolved significantly. Initial observations of lymphatic diseases provided the groundwork for recognizing distinct malignancies like cervical node cancer. Over the years, research has expanded through clinical trials and case studies, gradually illuminating the complexities of detection and treatment. Today, we stand at a crossroads where innovative treatment options are being explored, and the potential for more successful outcomes has never been greater.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Understanding cervical node cancer requires some fundamental knowledge of relevant terms:
- Lymph Nodes: Small, bean-shaped structures that are part of the lymphatic system, crucial for the immune response.
- Malignant Transformation: The process by which normal cells undergo genetic changes leading to uncontrolled growth and cancer.
- Diagnosis: The identification of the disease through various methods like imaging tests and biopsies.
- Therapeutic Approaches: The range of treatment methods including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
These terms help frame the discussion as we delve deeper into the characteristics of cervical node cancer, its signs, and how modern medicine addresses it.
“Knowledge is a powerful ally in the battle against cancer.”
“Knowledge is a powerful ally in the battle against cancer.”
This article promotes the belief that a well-informed patient and community can significantly enhance the journey through understanding and combating cervical node cancer.
Prolusion to Cervical Node Cancer
Cervical node cancer, a particular subset of cancers that manifests in the lymphatic system, is an area of growing concern in oncology. Understanding this type of cancer is not merely beneficial; it is vital — for patients, clinicians, and researchers alike. This section provides a foundational knowledge of cervical node cancer, laying the groundwork for a more nuanced exploration of its implications on health and well-being.
The focus here is on transcending beyond the mere pathology of the disease, delving into the complexities that influence its behavior and impact. An informed audience can better appreciate ongoing research efforts and support patient-centric approaches that enhance quality of life and treatment outcomes.
Defining Cervical Node Cancer
Cervical node cancer arises from malignant changes within the cervical lymph nodes, which are crucial components of the body’s immune system. Lymph nodes act as filters, trapping pathogens and cancer cells. When cancer strikes these nodes, it often signifies a more extensive health issue, piercing through the veil of local illness to hint at systemic implications.
Cervical node cancer is not a standalone condition but often links to other cancers, notably head and neck cancers. In some cases, it can emerge as a manifestation of metastatic disease, where cancer from another region spreads to the lymph nodes. This dynamic makes early detection significantly imperative, highlighting the need for vigilance among healthcare professionals.
"Understanding where cervical node cancer fits into the larger cancer landscape is instrumental for improved diagnostic and treatment strategies."
"Understanding where cervical node cancer fits into the larger cancer landscape is instrumental for improved diagnostic and treatment strategies."
Importance of Understanding the Disease
Grasping the intricacies of cervical node cancer facilitates a comprehensive perspective on its treatment and management.
- Clinical Awareness: Healthcare providers need to elucidate symptoms and signs associated with cervical node involvement, as these are often subtle and misinterpreted.
- Tailored Treatment: A deeper understanding can lead to more individualized therapies, addressing not just the cancer itself but also considering how it affects the patient’s overall health and mental well-being.
- Research and Development: The more we know about cervical node cancer, the better positioned we are to foster research that could lead to new treatments or preventive measures. In this regard, ongoing studies into genetic predispositions and environmental factors become essential for efficacious healthcare strategies.
- Public Awareness: On a broader scale, increasing public knowledge about cervical node cancer encourages early-stage detection, ultimately curbing the escalation of the disease.
In summary, defining cervical node cancer is only the tip of the iceberg. The importance of understanding this disease reverberates through various facets, influencing clinical guidelines, research orientations, and patient engagement. The next sections will build on this foundation, dissecting the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and the various avenues for therapeutic intervention that characterize cervical node cancer.
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Understanding the epidemiology and risk factors of cervical node cancer is not just critical for healthcare professionals but also essential for students, researchers, and policymakers as they seek to develop strategies for prevention and treatment. By gaining insights into how frequently this type of cancer occurs and the factors that contribute to its development, stakeholders can better prioritize research funding, public health initiatives, and educational programs aimed at raising awareness.
Prevalence and Incidence Rates
The prevalence and incidence rates of cervical node cancer can provide a valuable snapshot of its impact on the population. This malignancy is not commonly reported as a standalone cancer. Instead, it is often detected in conjunction with other cancers, particularly those associated with the head and neck region. In the United States, the incidence of lymphatic cancers, including cervical node cancer, has shown an upward trend in recent years, a finding linked to the increasing prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV).
Recent statistics show that approximately 55,000 new cases of head and neck cancers, including cervical lymph node involvement, are diagnosed annually. This statistic emphasizes the need for heightened awareness and proactive healthcare policies. Individuals might ignore a small swelling in the neck, but taking note of changing sizes or new growths can make all the difference in early diagnosis and successful treatment.
Genetic and Environmental Influence
Genetic factors play a notable role in the risk of developing cervical node cancer. Family history can increase susceptibility, with certain genetic mutations raising the likelihood of not only localized but also metastasized cancers. Variants in genes such as TP53 have been implicated in these conditions.
Additionally, environmental exposures significantly contribute to the likelihood of developing this form of cancer. Frequent exposure to pesticides, industrial solvents, and even second-hand smoke are environmental factors that have been correlated with higher rates of lymphoma and other cancers that could involve the cervical nodes.
Awareness of these factors can lead to better lifestyle choices and monitoring, as significant environmental risks can often be minimized through protective measures.
Behavioral Risk Factors
Some behavioral risk factorsalso markedly increase the chance of developing cervical node cancer. The following points should be noted:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking is one of the most significant behavioral risk factors associated with cervical node cancers. Smokers are at a heightened risk due to the numerous carcinogens inhaled.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinkers have a greater chance of developing various cancers, including those affecting the lymphatic system.
- Poor Diet: Diets lacking in fruits and vegetables can compromise the immune system, decreasing the body’s ability to fend off diseases, including cancer.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to obesity, which has been linked to a number of chronic diseases, including several types of cancer.
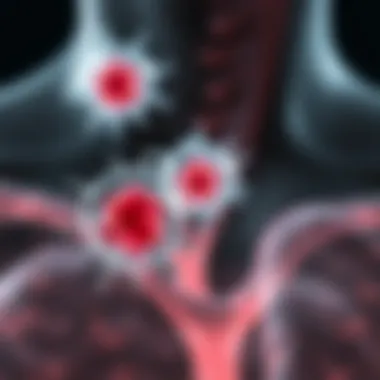
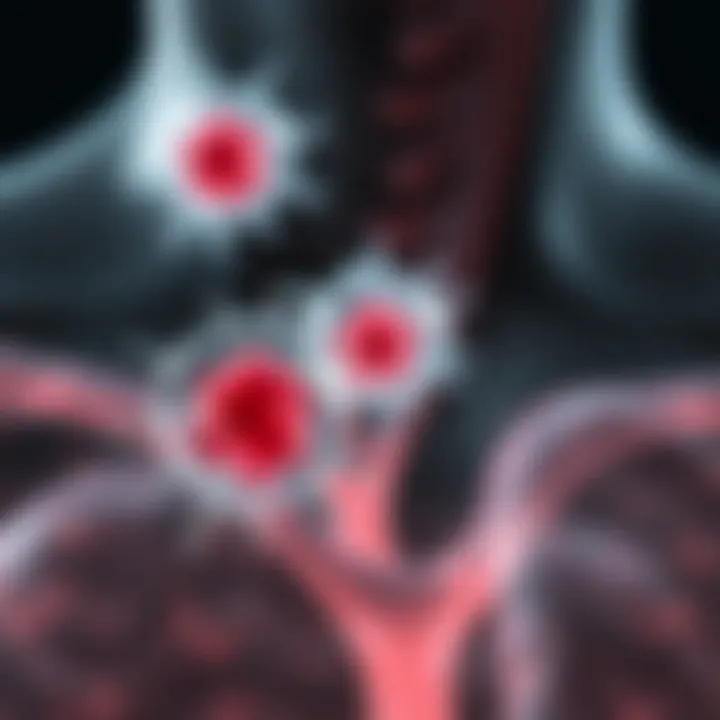
Addressing these modifiable risk factors through public health initiatives can lead to significant reductions in incidence rates, paving the way for better outcomes for patients.
"Prevention is better than cure" – recognizing risk factors offers a glimmer of hope in combating cervical node cancer.
"Prevention is better than cure" – recognizing risk factors offers a glimmer of hope in combating cervical node cancer.
For more information on cancer statistics and prevention strategies, visit CDC.gov or hope to learn something new at Cancer.org.
Pathophysiology of Cervical Node Cancer
Understanding the pathophysiology of cervical node cancer is crucial for comprehending how this illness manifests and progresses within the body. The cellular and molecular changes that occur in cervical lymph nodes are at the root of this malignancy, influencing not only its development but also its potential responses to treatment. This section sheds light on these critical mechanisms, providing a foundation for further exploration of therapeutic strategies.
Cellular Mechanisms of Tumor Development
Cervical node cancer often arises when normal cellular processes become dysregulated, leading to uncontrollable growth and division of cells. Several specific mechanisms play a role in this transformation:
- Genetic Mutations: The primary drivers of tumor development are mutations in critical genes involved in regulating cell cycle and apoptosis. For instance, mutations in oncogenes can promote excessive cell proliferation and survival, while tumor suppressor gene mutations can remove the natural brakes on cell division.
- Tumor Microenvironment: The microenvironment surrounding the lymph nodes is significant. Cancer cells can interact with neighboring healthy cells, causing a biochemical interplay that encourages growth. Cytokines and signaling molecules released by immune cells can create a conducive environment for tumor cell survival and proliferation.
- Immune Evasion: For a tumor to establish itself, it must evade the immune system's surveillance. Cancer cells can develop mechanisms to down-regulate antigen presentation and produce immunosuppressive factors, allowing them to persist and grow unchecked.
This multilayered process results in a chaotic environment within the lymph nodes, making early detection and intervention a critical aspect of managing cervical node cancer.
Lymphatic System and Cancer Spread
The lymphatic system plays a pivotal role in both the progression and metastasis of cervical node cancer. It serves not just as a network for immune response but as a pathway for cancerous cells to diffuse into other regions of the body. Key points regarding this process include:
- Lymphatic Drainage Patterns: Cancer cells can invade lymphatic vessels near the primary tumor site and disseminate to regional lymph nodes. Understanding these patterns can assist clinicians in predicting the likelihood of metastasis and tailor treatment strategies accordingly.
- Metastatic Cascade: Once the cancer cells are in the lymphatic vessels, they can spread unpredictably. This cascade can sometimes lead to distant metastases, complicating treatment and prognostic outcomes. For example, knowing that a tumor has spread to a specific set of lymph nodes can change staging dramatically, influencing the recommended course of therapy.
"The lymphatic system, often seen as an inert highway, is a key player in the journey of cancer, turning into a vessel of opportunity for malignant cells to navigate and colonize distant sites."
"The lymphatic system, often seen as an inert highway, is a key player in the journey of cancer, turning into a vessel of opportunity for malignant cells to navigate and colonize distant sites."
Through understanding these mechanisms, researchers and clinicians can devise targeted methods that inhibit tumor growth and metastasis. Consequently, a deeper grasp of the pathophysiology unveils opportunities for innovative treatments and a clearer direction for ongoing research.
For more information, explore National Cancer Institute and American Cancer Society.
Clinical Manifestations
Understanding the clinical manifestations of cervical node cancer serves as a linchpin in the early detection and management of this disease. Recognizing the signs and symptoms can lead to prompt intervention, significantly impacting outcomes. Given the intricacies involved, the clinical expressions of this cancer can vary widely, not only among individuals but also based on the stage and overall health of the patient. By translating these manifestations into actionable insights, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions that enhance patient care.
Common Symptoms to Observe
Awareness of specific symptoms associated with cervical node cancer is crucial for timely diagnosis. The clinical symptoms typically include:
- Swelling in the Neck: Often the most noticeable sign, enlarged lymph nodes can create visible lumps. Patients may feel these nodes as they progress.
- Pain in the Neck or Throat: Often described as persistent and unexplained, this pain may accompany swallowing or even during regular movements of the head.
- Changes in Voice: Alterations in one’s vocal tone or hoarseness could arise as a result of pressure on nearby structures in the neck.
- Fever and Night Sweats: Systemic symptoms may emerge due to an ongoing inflammatory response, reflecting the body's attempt to combat the malignant cells.
- Unintentional Weight Loss: A significant, unexplained drop in weight can indicate that cancer cells are escalating their metabolic demands on the body.
Potentially, these symptoms could align with various other health conditions, making distinction imperative. Thus, vigilance in monitoring these signs is essential for individuals at risk.
Differences Among Patient Demographics
Cervical node cancer affects individuals differently, influenced heavily by demographic factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, and overall health status. Age plays a pivotal role; for instance, younger patients might present with more aggressive forms of the disease, whereas older adults could experience a slower progression.
Moreover, gender differences also come into play; some studies suggest that men are more likely to develop specific types of cervical cancer compared to women, perhaps due to variances in risk behaviors or biological factors. Additionally, ethnic background can influence both the type and the frequency of symptoms experienced. Certain groups may have genetic predispositions that result in distinctive manifestations.
The psychosocial aspect shouldn't be overlooked; individuals from different backgrounds might interpret or report symptoms variably. Cultural perceptions of health, access to healthcare, and even social stigmas can impact how symptoms are acknowledged and addressed.
Ultimately, these demographic disparities underscore the need for tailored approaches in diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing that there is no one-size-fits-all can lead to more personalized and effective healthcare strategies.
"Recognition of early symptoms in cervical node cancer is similar to lighting a beacon in the dark; it can guide patients towards timely intervention and potentially life-saving care."
"Recognition of early symptoms in cervical node cancer is similar to lighting a beacon in the dark; it can guide patients towards timely intervention and potentially life-saving care."
By keeping an eye on these symptoms and being attuned to demographic differences, both healthcare professionals and patients can navigate the complexities surrounding cervical node cancer more effectively, ultimately enhancing outcomes and expectations.
Diagnostic Approaches
The detection and diagnosis of cervical node cancer is a crucial step in managing the disease effectively. Diagnostic approaches serve not merely as formalities; they can significantly influence treatment pathways and outcomes for patients. By adopting a comprehensive strategy that includes initial assessments, imaging, and biopsy, clinicians can attain a clearer understanding of a patient’s condition. This multi-faceted diagnosis contributes to higher rates of successful treatment, making it imperative to recognize the integration of these elements.
Initial Assessment and History Taking
Initial assessment is the stepping stone in the diagnostic journey. It starts with thorough history taking, where healthcare providers gather crucial information about the patient. This typically includes:
- Personal Medical History: Understanding prior illnesses can illuminate potential risk factors.
- Symptomatology: Detailing present symptoms — such as swelling, pain, or any noticeable abnormality — is vital.
- Family History: A familial link to cancer can heighten suspicion for cervical node malignancy.
During this phase, the doctor performs a physical examination, focusing primarily on palpating the lymph nodes. If any abnormal growth or tenderness is experienced, it raises the flag for further evaluation.
"The power of early diagnosis cannot be overstated; knowing where we stand with our health is a half victory in any battle against disease."
"The power of early diagnosis cannot be overstated; knowing where we stand with our health is a half victory in any battle against disease."
Imaging Techniques Utilized
Once the initial assessment indicates potential malignancy, imaging techniques come into play. These modalities provide visual insights into the anatomical changes taking place within the cervical region. Some prevalent imaging techniques include:


- Ultrasound: A tech that utilizes sound waves to produce images of the lymph nodes; it's non-invasive and efficient.
- CT Scan: This technique captures cross-sectional images, offering detailed information about the size and location of lymph nodes.
- MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging provides finer details, particularly beneficial in assessing the extent of the disease.
Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, often necessitating a combination for the most accurate diagnosis. The choice of imaging depends on factors like availability, cost, and patient condition, further underscoring the importance of personalized diagnostic pathways.
Biopsy and Histopathological Examination
After imaging, if suspicion still looms large, a biopsy becomes essential. This procedure involves taking a small sample of lymph tissue for histopathological examination. The histopathologist examines this sample under a microscope to confirm the presence (or absence) of cancerous cells. There are several types of biopsy methods:
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB): A less invasive option, FNAB provides quick results and can be performed in an outpatient setting.
- Core Needle Biopsy: Offers larger samples but is slightly more invasive than FNAB.
- Excisional Biopsy: Involves removing an entire lymph node, allowing for extensive examination.
Histopathology is pivotal as it confirms not just the presence of cancer but also determines the type and grade, which are paramount for therapy decisions.
The combined effectiveness of initial assessments, imaging, and biopsy contributes significantly to developing a precise diagnosis. This multifaceted approach ensures that individuals facing cervical node cancer receive timely and tailored treatment plans.
Staging and Classification
Understanding the staging and classification of cervical node cancer is a cornerstone in managing patient care effectively. The stage of the cancer at the time of diagnosis greatly influences treatment plans and prognoses. In particular, accurate staging helps clinicians determine how far the cancer has spread and what resources will best serve the patient's needs. Staging systems provide a structured way to communicate the extent of the disease among healthcare professionals, ultimately enhancing treatment outcomes.
Staging Systems Explained
Staging systems are used to categorize cancers based on their characteristics and the severity of the disease. For cervical node cancer, the most commonly utilized system is the AJCC (American Joint Committee on Cancer) TNM staging system. This system evaluates three critical components:
- T (Tumor): Refers to the primary tumor's size and extent. For cervical node cancer, it indicates whether the malignant cells are confined to the lymph nodes or if they invade nearby structures.
- N (Nodes): This component looks at regional lymph node involvement, detailing how many nodes are affected and if there is spread beyond the immediate area.
- M (Metastasis): This aspect assesses whether the cancer has metastasized to distant organs or tissues.
Following this system allows for a more tailored approach to treatment, as treatments can vary significantly depending on whether the cancer is localized to the lymph nodes or has spread elsewhere. Additionally, understanding staging can assist in determining eligibility for clinical trials, where new innovative treatments may be available based on disease classification.
Importance of Accurate Staging
Accurate staging of cervical node cancer cannot be understated. Firstly, it establishes a common language among healthcare providers, facilitating better care coordination. When everyone understands the specifics of the case, it leads to more informed decision-making, whether in surgery, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy.
It is also vital for predicting patient outcomes. Generally, early-stage cancers (stage I or II) have better survival rates compared to those diagnosed at stage III or IV. This knowledge gives patients clarity on their situation, which is essential for mental readiness as they navigate treatment options. Moreover, monitoring the progression through accurate staging helps healthcare providers adjust treatment as necessary, aiming to optimize quality of life and survival rates for patients.
"Accurate staging is not just a number but a vital tool that shapes our approach, decisions, and ultimately, patient outcomes".
"Accurate staging is not just a number but a vital tool that shapes our approach, decisions, and ultimately, patient outcomes".
Therapeutic Strategies
Therapeutic strategies play a pivotal role in managing cervical node cancer. Understanding these approaches is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions. Each strategy has its unique benefits and considerations that can significantly impact patient outcomes. By tailoring treatment to the individual needs of each patient, the goals of improving survival rates and enhancing quality of life can be better achieved.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions are often the first line of attack in cervical node cancer treatment. This can range from lymphadenectomy, where the affected lymph nodes are surgically removed, to more extensive procedures depending on the cancer's stage and spread.
- Benefits: Surgical removal of malignant tissues can lead to clear margins and reduce the overall tumor burden. In many cases, patients experience a significant reduction in symptoms and can find relief from physical discomfort.
- Considerations: However, surgery isn't without risks. Potential complications may arise, including infections, bleeding, and changes in lymphatic drainage. The decision to proceed with surgery requires a thorough assessment of the patient's overall health and cancer stage.
Radiation Therapy Techniques
Radiation therapy is another cornerstone in the management of cervical node cancer. It can be utilized either post-surgery to eliminate any residual cancer cells or as a primary treatment in non-surgical candidates.
- Methods: Techniques like external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) are commonly employed. These methods allow for precise targeting of cancerous areas while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Benefits: This reduces the risk of treatment-related side effects and enhances the therapeutic effect on the tumor. Radiation can also serve as palliative treatment, providing relief from symptoms in advanced cases.
Chemotherapy Protocols
Chemotherapy involves using chemical substances to kill fast-growing cancer cells. This can either be used independently or in conjunction with surgery and radiation.
- Protocols: Common regimens include cisplatin and carboplatin, often combined with other drugs such as paclitaxel or 5-FU depending on individual cases.
- Considerations: While chemotherapy can be effective, it comes with its own set of side effects, including nausea, fatigue, and immunosuppression. Thus, it demands careful monitoring and management of symptoms throughout the treatment process.
- Benefits: The combination therapy tends to enhance treatment efficacy, tackling cancer from multiple fronts, and minimizing the chances of metastasis.
Emerging Therapies and Clinical Trials
Innovation in cancer treatment is ongoing, with numerous promising therapies rolling out from research pipelines. Clinical trials often serve as a gateway for patients to access cutting-edge treatment options.
- Examples of Emerging Therapies: Immunotherapy, which harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer, is gaining ground. Treatments like checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapy are under rigorous investigation.
- Engagement in Trials: Patients interested in clinical trials can contact oncology centers or universities conducting research, ensuring they explore all viable options.
- Benefits: These new approaches can offer hope when traditional therapies have failed. They often aim to achieve more durable responses with potentially fewer side effects.
"Understanding therapeutic strategies isn't just about treatment; it's about crafting a personalized approach that aligns with patients' unique circumstances."
"Understanding therapeutic strategies isn't just about treatment; it's about crafting a personalized approach that aligns with patients' unique circumstances."
This commitment to tailored therapeutic strategies embodies not just clinical necessity but also the compassionate aspect of patient care.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates for cervical node cancer plays a pivotal role in shaping patient care strategies and informing treatment decisions. Prognosis refers to the likely outcome of the disease, influenced by various factors unique to each individual. It offers patients and their families a glimpse into what they might expect throughout the course of their illness and treatment. This section covers the key aspects and implications of prognosis and survival rates for cervical node cancer, emphasizing that accurate prognostication is crucial not only for patients but also for healthcare providers involved in managing this condition.
Factors Influencing Outcomes
A variety of determinants can affect the outcomes of cervical node cancer, making each patient's situation distinct. Here are some prominent factors:
- Stage of the Cancer: The extent to which the cancer has spread significantly impacts survival rates. Early-stage detection generally correlates with better outcomes.
- Patient’s Age: Younger patients often exhibit more favorable prognoses when compared to older individuals. The body's ability to heal and respond to treatments varies with age, influencing overall outcomes.
- Histopathology: The characteristics of the tumor cells themselves—such as their differentiation and the presence of specific markers—can dictate the aggressiveness of the cancer and subsequently affect survival.
- Overall Health and Co-morbid Conditions: A patient's general health and any existing medical conditions can set the stage for how well they respond to treatment, ultimately influencing survival rates.
- Treatment Protocols: The strategies employed, including surgical interventions, chemotherapy regimens, and radiation targeting, play a crucial role in determining the success of combating cervical node cancer.
Ultimately, recognizing these factors not only aids healthcare professionals in managing treatment plans but also empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care, fostering a partnership in health management.
Ultimately, recognizing these factors not only aids healthcare professionals in managing treatment plans but also empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care, fostering a partnership in health management.
Long-term Follow-Up and Care
Long-term follow-up care is vitally important for patients recovering from cervical node cancer. Regular monitoring helps in the early detection of any potential recurrences, while also providing a platform for addressing ongoing physical and psychological concerns. Benefits of consistent follow-up include:
- Enhanced Monitoring: Regular check-ups and imaging can catch any signs of cancer returning, allowing for timely interventions.
- Management of Side Effects: Treatment for cervical node cancer, like any cancer treatment, can lead to side effects that require attention. Follow-up care provides support in managing these effects effectively.
- Psychosocial Support: Regular interactions with healthcare providers can reduce feelings of isolation among patients. Addressing mental health matters and facilitating support systems are part of comprehensive follow-up care.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Medical teams can guide patients on lifestyle modifications that can bolster recovery and improve quality of life, covering diet, exercise, and stress management.
The unique journey of each cervical node cancer patient underscores the necessity for personalized follow-up care. This ensures a holistic approach to recovery and enhances the potential for better long-term outcomes.
Psychosocial Implications
Understanding the psychosocial implications of cervical node cancer is essential, as it sheds light on the intricate web of challenges faced by patients and their families. This section delves into the significant impact cancer has not just on physical health but also on emotional and social well-being. Patients often find themselves grappling with an unexpected emotional tide that can strain personal relationships and affect overall quality of life. It is crucial for healthcare providers and support networks to be aware of these issues, ensuring that care extends beyond the hospital walls.
Impact on Mental Health
A diagnosis of cervical node cancer doesn't merely introduce a physical ailment; it can trigger a mental health storm. Patients may experience a plethora of emotions ranging from anxiety to depression following the news of their condition. The unpredictability of treatment outcomes and the fear of mortality lurk in the background, casting shadows on their emotional landscape.
Additionally, the stress of adjusting to life after diagnosis can be monumental. Many individuals report feelings of isolation, as it’s common for friends and family to struggle with knowing how to offer support. This can lead to a sense of abandonment or alienation for patients who may feel that their issues are not understood or acknowledged. Studies suggest that those with solid mental health support are often better prepared to face not only the physical challenges but also the psychological hurdles that come their way.
- Increased anxiety: Uncertainty about treatment effectiveness can lead to persistent worry.
- Depression prevalence: A significant number of patients report feelings of sadness or hopelessness, affecting their willingness to engage in everyday activities.
- Social withdrawal: Some individuals may distance themselves from social interactions, further exacerbating feelings of loneliness.
“Mental health is just as important as your physical health. It’s all connected.”
Social Support Mechanisms
Having a robust support system can dramatically influence a patient’s ability to cope with cervical node cancer. Social support may come in various forms, such as family, friends, or support groups. Here’s how each plays a pivotal role:
- Family Involvement: Family can provide emotional and practical support. Simple acts, like accompanying patients to treatment sessions or helping with daily chores, can alleviate stress and foster a sense of normalcy.
- Peer Support Groups: Connecting patients with others who are facing similar battles can be a lifeline. These groups offer a forum for sharing experiences, fears, and coping strategies in a safe environment. Participants often find solace in knowing they are not alone.
- Professional Counseling: Sometimes, the issues run deeper than friends and family can address. In such cases, professional therapists can provide guidance on dealing with emotional turmoil and anxiety. Therapy sessions tailored specifically to patients with cancer can offer coping mechanisms that fit their unique challenges.
Recognizing and implementing these support mechanisms can significantly enhance a patient's emotional resilience, paving the way for a more balanced approach to treatment and recovery. As such, integrating mental health considerations into treatment plans is vital in managing not just the disease, but the overall well-being of individuals affected by cervical node cancer.
For further reading on psychosocial effects and support mechanisms, you might find these resources useful:
This comprehensive understanding of psychosocial implications lays a foundation for better support structures, ultimately improving the quality of life for patients battling cervical node cancer.
Future Directions in Research
Research on cervical node cancer is on the cusp of significant advancements. The rapid evolution of oncological studies has ushered in a new era of understanding, promising to address this complex condition comprehensively. Focusing on future avenues in research is crucial because it ensures that the battle against cervical node cancer evolves in tandem with our growing scientific acumen. The integration of cutting-edge technologies and methodologies holds the potential to improve diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic outcomes for affected individuals.
Innovative Therapeutics Development
As we explore innovative therapeutics development, it's pivotal to recognize the transformative impact of targeted therapies and immunotherapies on cancer treatment paradigms. Unlike conventional treatments, which often take a one-size-fits-all approach, targeted therapies aim to attack specific molecular alterations that characterize cervical node cancer. This specificity not only enhances the efficacy of treatment but also minimizes collateral damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
For instance, the advent of small-molecule inhibitors that disrupt cancer cell signaling pathways is an exciting area of focus. Recent studies are evaluating how these agents can lead to better patient responses and longer survival rates. Moreover, combining such treatments with immunotherapeutic approaches is producing promising results.
"Innovative therapies stand to shift the paradigm of cervical node cancer treatment, enabling more tailored and effective strategies."
"Innovative therapies stand to shift the paradigm of cervical node cancer treatment, enabling more tailored and effective strategies."
The exploration of combination therapies can produce synergistic effects, augmenting the capacity of the immune system to recognize and eliminate malignant cells. Collaborations between academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies are vital in this respect, as they facilitate the testing of novel agents and combinations in clinical trials. Thus, ongoing efforts in this realm are essential to find effective solutions and improve outcomes for patients.
Role of Personalized Medicine
Another promising direction in cervical node cancer research is the application of personalized medicine. With the rapid advancements in genomics, we can tailor treatment strategies based on a patient’s unique genetic profile. This precision means that decisions concerning therapy can be informed by the specific mutations in a patient’s tumor, leading to a more effective and less toxic treatment plan.
There is a growing body of research focused on biomarkers that predict how well individual patients will respond to certain therapies. The use of genetic testing to determine an individual's risk for concurrent cancers and to tailor surveillance plans is becoming more important. This approach not only enhances patient outcomes but also fosters a stronger compliance between medical professionals and patients, as therapy becomes increasingly relevant to the individual.
Furthermore, incorporating machine learning algorithms can assist in identifying patterns in treatment responses and eventual outcomes. Analyzing vast amounts of data can uncover variables that influence therapy effectiveness, leading to tailored treatment plans based on empirical evidence rather than a generalized approach.
Culmination
As we wrap up this rich exploration of cervical node cancer, we find ourselves at a pivotal juncture in understanding this complex disease. Recognizing the significance of awareness and ongoing research cannot be overstated. Each element discussed in this article plays a crucial role in illuminating the path forward for patients, medical professionals, and researchers alike.
Summary of Key Points
Here, we can summarize the primary insights into cervical node cancer:
- Definition and Etiology: Cervical node cancer is instigated by malignant changes within the lymph nodes, often stemming from systemic cancers.
- Risk Factors: A mix of genetic predispositions and environmental factors elevate the risk, including long-term smoking and family history.
- Clinical Manifestations: Symptoms can range from swollen lymph nodes to unexplained fever and night sweats, necessitating prompt clinical attention.
- Diagnostic Techniques: Early diagnosis hinges on a blend of imaging technologies and biopsy procedures that provide a clearer picture of the tumor's nature.
- Therapeutic Options: Patients are presented with a spectrum of therapeutic choices, from surgical interventions to emergent therapies currently under clinical investigations.
- Prognosis and Follow-Up: Understanding prognosis is complicated by numerous factors, including overall health and tumor stage. Continuous follow-up is essential to manage long-term health.
- Psychosocial Implications: The emotional toll of a cancer diagnosis is profound, highlighting the need for adequate social support and mental health resources.
Call for Ongoing Research and Awareness
The journey does not end with what we know today. For a condition like cervical node cancer, the quest for knowledge must be relentless. As the medical community forges ahead, it's vital to invest in innovative research and clinical trials. These efforts can pave the way for breakthroughs in treatment and management.
Furthermore, increasing public awareness is equally important. Initiatives that educate the public on symptoms and risk factors can lead to earlier diagnoses, improving outcomes significantly.
"Awareness is the first step; understanding how to act on it is what drives change."
"Awareness is the first step; understanding how to act on it is what drives change."
In light of this, we must all come together—researchers, healthcare providers, patients, and society—to foster an environment conducive to learning, understanding, and ultimately conquering cervical node cancer.



