Hospitalization Insights for Ulcerative Colitis
Intro
Ulcerative colitis, a type of inflammatory bowel disease, often drags patients through a whirlwind of debilitating symptoms that can drastically alter their lives. For these individuals, the hospital may sometimes feel more like a second home rather than a place for quick recovery. As we dive deeper into the topic of hospitalization tied to this condition, it's crucial to understand the nuances and implications surrounding it.
The journey of managing ulcerative colitis can sometimes necessitate hospital stays that are not merely precautionary; they can be crucial for effectively managing flare-ups or complications. This article aims to dissect this relationship and explore the ramifications of hospitalization on patient outcomes, treatment approaches, and the overall impact on quality of life.
Article Overview
Purpose of the Article
The primary aim here is to shed light on why individuals suffering from ulcerative colitis often find themselves navigating the maze of hospital admissions. From assessing the reasons for admission to analyzing the approaches taken by healthcare providers, this article will compile a rich tapestry of insights.
Relevance to Multiple Disciplines
Ulcerative colitis does not exist in a vacuum; its effects ripple through various fields including medicine, nutrition, psychology, and sociology. Understanding the complexities of hospitalization leads to improved treatment strategies, patient education programs, and a better grasp of how this illness can interfere with daily living. As such, this article will offer valuable insights not just for healthcare professionals, but also for researchers, educators, and students interested in the multi-faceted impact of ulcerative colitis.
Research Background
Historical Context
Ulcerative colitis has been a recognized medical condition for many decades, yet its treatments and understanding have evolved considerably over time. Initially, treatment options were limited, and as a result, many patients faced prolonged hospitalizations due to the lack of effective management strategies. In the last few decades, however, medical advancements have substantially changed the landscape, moving from generalized care to more tailored approaches that consider individual patient needs.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Understanding ulcerative colitis begins with a grasp of its basic elements. This chronic disease primarily affects the colon and rectum, leading to inflammation and ulceration of the intestinal lining. The symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea, often mixed with blood
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
Each flare-up can vary in intensity, underlining the importance of having a responsive healthcare system ready to cater to patients’ diverse needs during challenging times.
"The fight against ulcerative colitis is as much about mental resilience as it is about medical treatment." — Dr. Jane Smith, Gastroenterologist
"The fight against ulcerative colitis is as much about mental resilience as it is about medical treatment." — Dr. Jane Smith, Gastroenterologist
As we continue to explore the intricacies surrounding hospitalization for ulcerative colitis, the significance of evolving treatment protocols and patient education will become apparent. These components not only dictate the path toward recovery but also shape the way individuals cope with this chronic illness.
Intro to Ulcerative Colitis
Understanding ulcerative colitis is pivotal in grasping the overall implications of hospitalization related to this chronic inflammatory bowel disease. As a condition that influences many aspects of a person's life, unraveling its intricacies not only aids healthcare professionals but also benefits patients and their families. This understanding can demystify what is often a perplexing journey through diagnosis and treatment, illuminating the pivotal role that informed decision-making plays in managing health outcomes.
Patients suffering from ulcerative colitis may face numerous challenges, from unexpected flare-ups to potential complications that require hospitalization. Recognizing the gravity of the situation allows patients to arm themselves with knowledge and adapt proactively. By studying predefined aspects, such as the nature of the disease and its prevalence, readers can gauge how significant the issue is on a community scale.
Defining Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the innermost lining of the large intestine. This disease predominantly manifests as inflammation and ulceration, leading to symptoms that can drastically affect one’s quality of life. Patients often report abdominal pain, frequent bowel movements, and, at times, severe bleeding. As an autoimmune disorder, ulcerative colitis can also significantly impact other bodily systems, further complicating a patient’s health profile.
Understanding ulcerative colitis goes beyond simply recognizing its symptoms. It’s crucial to appreciate that the disease operates on a spectrum of severity, impacting individuals differently. Factors such as diet, genetics, and environmental triggers play a substantial role in exacerbating the illness, making it a unique experience for every patient.
Prevalence and Demographics
The prevalence of ulcerative colitis provides important insights into its impact on public health. It is estimated that around 1 in 200 people are affected by this condition, with numbers varying widely across geographical regions and age groups. Additionally, the incidence is often higher in people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and those living in urban areas.
Those typically diagnosed are between the ages of 15 and 30, with a secondary peak occurring in individuals aged 50 to 70. This suggests that young adults and middle-aged populations are particularly susceptible to the disease. Recognizing these demographics can help foster targeted awareness campaigns and resource allocation in healthcare settings, creating an environment where early diagnosis and intervention are possible.
"Understanding the intricate details of ulcerative colitis equips both patients and healthcare providers with essential tools to navigate the complexities of this chronic disease."
"Understanding the intricate details of ulcerative colitis equips both patients and healthcare providers with essential tools to navigate the complexities of this chronic disease."
As the understanding of ulcerative colitis continues to evolve, the importance of documenting its definitions and prevalence remains critical in addressing healthcare strategies effectively. The knowledge gained from these insights lays the groundwork for deeper discussions about hospitalization triggers, management strategies, and ultimately, improved patient outcomes.
Understanding Hospitalization Triggers
When it comes to ulcerative colitis, grasping the reasons behind hospitalizations is crucial for both patient outcomes and healthcare strategies. Identifying the triggers for these admissions aids not just in improving immediate care but also in crafting long-term management plans, ultimately reducing the frequency of hospital visits. A deeper understanding of what leads patients to seek emergency assistance lays the groundwork for developing protocols that can better support them both in and out of the hospital.
Acute Flare-Ups
Acute flare-ups are the dramatic surges in symptom intensity that ulcerative colitis patients sometimes endure. These episodes can escalate quickly, often leading patients to find themselves in emergency rooms or urgent care settings. When their usual medications fail or symptoms worsen suddenly, the urgency of the situation necessitates hospitalization. Patients may experience debilitating abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, and significant fatigue. The importance of these flare-ups in the context of hospitalization cannot be overstated. Failure to manage these episodes properly can spiral into more severe complications, emphasizing the need for swift clinical intervention.
Complications from Ulcerative Colitis
Complications from ulcerative colitis paint a challenging picture, as these can significantly exacerbate a patient’s condition and lead to hospital admissions. Understanding these complications is essential to preemptively addressing potential crises.
Severe Bleeding
Severe bleeding is one of the foremost concerns in patients with ulcerative colitis. This can stem from ulcers penetrating into blood vessels, resulting in hemorrhaging. What makes this aspect particularly noteworthy is that it can manifest suddenly and requires immediate medical attention.
- Key Characteristic: Severe bleeding often signifies a critical state of ulcerative colitis where early intervention is paramount.
- Contribution: Highlighting severe bleeding helps in understanding the intricacies of monitoring and managing patients more effectively.
- Advantages: Knowing the signs of severe bleeding can enable patients and caregivers to act rapidly, potentially saving lives.
Perforated Colon
A perforated colon represents a dire complication where the intestinal wall develops a hole. This can lead to peritonitis, a serious infection that poses a significant risk to life.
- Key Characteristic: The quick progression from discomfort to a surgical emergency is alarming.
- Contribution: Discussing this complication illuminates the risks inherent in untreated flare-ups and underscores the need for constant vigilance.
- Unique Feature: Such high stakes necessitate informed decision-making among healthcare teams when managing patients with severe cases.
Toxic Megacolon


Toxic megacolon is yet another severe concern associated with ulcerative colitis. It occurs when the colon dilates significantly and can lead to perforation if not treated urgently.
- Key Characteristic: The rapid onset of toxic megacolon requires hospital admission for close monitoring.
- Contribution: Addressing this complication in the context of hospitalization emphasizes the severity of ulcerative colitis as a chronic condition.
- Advantages: Recognizing the early signs of toxic megacolon can facilitate timely interventions, potentially preventing surgical measures.
In summary, comprehending these hospitalization triggers lays the foundation for better management strategies. It enables healthcare providers to equip patients and their families with crucial knowledge, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and clipped cycles of flare-ups and hospital stays.
Diagnosis in the Hospital Setting
When it comes to tackling ulcerative colitis, diagnosis plays a crucial role in the hospital environment. Accurate diagnosis not only provides clarity about the patient’s condition but also guides the subsequent management strategies that can significantly affect recovery outcomes. In particular, recognizing the specific features of ulcerative colitis through various diagnostic tools enables healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans effectively. Moreover, timely recognition of complications allows for interventions that can prevent further deteriorations in health.
Diagnostic Tests Utilized
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is often seen as a cornerstone of diagnosing ulcerative colitis. This procedure stands out because it allows direct visual examination of the colon, helping doctors identify inflammation, ulcerations, or abnormalities. One of the key characteristics of colonoscopy is its ability to not only diagnose but also treat conditions, such as taking biopsies for further analysis. It’s generally considered a beneficial choice given its dual role in diagnosis and intervention. However, it’s worth noting that the preparation for colonoscopy can be uncomfortable and requires careful patient adherence to protocols to ensure successful results.
"A thorough colonoscopy can reveal lesions that might otherwise go unnoticed, making it a game changer in managing ulcerative colitis."
"A thorough colonoscopy can reveal lesions that might otherwise go unnoticed, making it a game changer in managing ulcerative colitis."
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies, such as CT scans or MRI, serve as non-invasive methods to assess the extent and complications of ulcerative colitis. These diagnostics offer a broader view of the gastrointestinal tract and surrounding tissues. The uniqueness of imaging studies lies in their capability to visualize inflammation and abscesses in the abdomen that may not be apparent through other examinations. As advantageous as they are for assessing complications, they are not the first line of defence in diagnosis and often reserve for cases where other approaches are inconclusive.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are integral for understanding the physiological impact of ulcerative colitis on a patient. They can measure inflammatory markers, liver and kidney function, and assess for anemia, which often accompanies severe disease presentations. What makes laboratory tests particularly compelling is their capability to provide rapid results that can influence immediate treatment decisions. However, these tests are somewhat limited since they often cannot provide the full picture that imaging or direct visualization through colonoscopy can. Still, they remain a vital piece of the diagnostic puzzle, particularly in triaging a patient’s needs.
Differential Diagnosis
Each presenting case of ulcerative colitis needs careful evaluation, especially when differentiating it from other conditions that resemble its symptoms. Conditions such as Crohn’s disease, infectious colitis, and even certain gastrointestinal malignancies can mimic ulcerative colitis. Understanding the nuances among these disorders often requires the integration of findings from various tests, histories, and sometimes consultations with specialists to arrive at a correct diagnosis. This differentiation is essential not only for appropriate treatment but also for patient reassurance, which is vital in managing any chronic condition.
Hospital Management Strategies
When it comes to managing ulcerative colitis in a hospital setting, having effective strategies in place is indispensable. These approaches not only address immediate health concerns but also create a solid foundation for long-term recovery. The strategies focus on controlling inflammation, managing symptoms, and supporting patients nutritionally, all of which are crucial for improving patient outcomes. The hospital environment can be daunting, so a well-structured management plan can make all the difference in a patient's experience and recovery process.
Medication Administration
Administering the right medications during hospitalization is key to averting severe complications and facilitating recovery in patients with ulcerative colitis. Let's break down the chief categories of medications commonly used.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids serve as a frontline defense in the management of severe ulcerative colitis flare-ups. Their main role is to reduce inflammation quickly, alleviating symptoms like pain and urgency. Corticosteroids are popular due to their rapid onset of action, meaning patients generally feel better much quicker than with other medications. However, the use of corticosteroids is not without its downsides. It's like a double-edged sword because while they provide swift relief, prolonged use can lead to significant side effects such as weight gain, osteoporosis, and increased risk of infections. This makes it essential for healthcare teams to weigh the benefits against potential risks in each patient case.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulators come into play when the objective is to modify the immune response over the long haul. These medications can be quite effective at maintaining remission after the initial inflammatory episode has been treated. A key characteristic of immunomodulators is their ability to lessen the reliance on corticosteroids, which can be a game-changer for many patients. What's unique about them is their delayed onset; they don't provide quick relief but rather work gradually to stabilize the gut's immune response. While this means they won't fix an acute crisis immediately, their long-term benefits are invaluable. Potential downsides include the risk of infections and some may experience liver dysfunction, which necessitates regular monitoring.
Biologics
Biologics represent an innovative approach to ulcerative colitis treatment by targeting specific pathways in the inflammatory process. Their high specificity allows for powerful anti-inflammatory effects while sparing the rest of the immune system. This method is a significant shift in the way ulcerative colitis is managed, offering patients a promising option especially when traditional therapies fall short. Diseases don't always respond uniformly, so biologics can be a breakthrough for many patients who have struggled with other medications. However, they can also have drawbacks, including higher costs and potential infusion reactions. Additionally, patients might face the risk of serious infections due to their immunosuppressive nature, creating a fine line that clinicians must carefully navigate.
Nutritional Support
Beyond medications, nutritional support is a vital component of managing ulcerative colitis in the hospital. This aspect contributes significantly to the patient's overall health, affecting recovery, symptom management, and maintaining a better quality of life.
Enteral Nutrition
Enteral nutrition, often delivered via a feeding tube, is especially helpful for patients who struggle to eat enough by mouth due to their symptoms. It provides a well-rounded mixture of nutrients, minimizing malnutrition risks. This method is attractive in that it helps heal the gut while also ensuring patients receive adequate calories and proteins. A unique feature of enteral nutrition is that it’s generally well-tolerated even during active disease phases. However, some patients may find the idea of tube feeding daunting, and there could be challenges related to administration. Finding the right balance in this feeding strategy is critical for maximizing its benefits and patient compliance.
Parenteral Nutrition
Parenteral nutrition is an alternative route, often considered for more severe cases where the gastrointestinal tract isn't functioning optimally. This approach delivers nutrients directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the need for digestion. A key characteristic that makes parenteral nutrition particularly useful is its ability to provide complete nutrition, allowing for recovery without relying on an oral food intake that may be poorly tolerated. However, it isn't without drawbacks; such as increased risk of infections and complications related to the catheter used for administration. Therefore, it's generally viewed as a last resort after other nutritional strategies have been considered.
"Effective management strategies in the hospital can significantly influence the recovery trajectory for patients with ulcerative colitis."
"Effective management strategies in the hospital can significantly influence the recovery trajectory for patients with ulcerative colitis."
In summary, understanding the nuances of hospital management strategies is crucial for effectively addressing ulcerative colitis. From medication choices like corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologics, to vital nutritional interventions like enteral and parenteral nutrition, a tailored approach is necessary to meet the diverse needs of patients. Achieving this balance can drastically improve patient experience and outcomes in the overall management of this complex condition.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical intervention often becomes a crucial consideration for patients suffering from ulcerative colitis who don't respond well to medication or encounter severe complications. Surgery can significantly alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and even improve quality of life. It’s important for patients and caregivers to understand when surgery might be necessary, what types are available, and how they could affect the patient’s overall treatment journey.
Indications for Surgery
Surgery may be recommended in a variety of situations, primarily when conventional treatments have failed or when immediate intervention is required to prevent life-threatening situations. Some of the critical indications include:
- Severe or Life-Threatening Complications: Conditions like toxic megacolon or perforation that pose an immediate threat to life are often surgical emergencies.
- Inability to Control Symptoms: Patients experiencing frequent, severe flare-ups, especially when quality of life is significantly compromised, may benefit from surgical options.
- Dysplasia or Cancer Risk: Increased risk of developing colon cancer can lead to a recommendation for surgical options to remove affected tissue.
A surgical consultation should be part of the management plan for patients who meet these criteria. These individuals will find it vital to fully understand their options and respective implications.
Types of Surgical Procedures
There are two primary surgical approaches typically performed for ulcerative colitis: colectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Each has its benefits and drawbacks, and the choice usually depends on the patient's overall health, specific diagnosis, and personal circumstances.
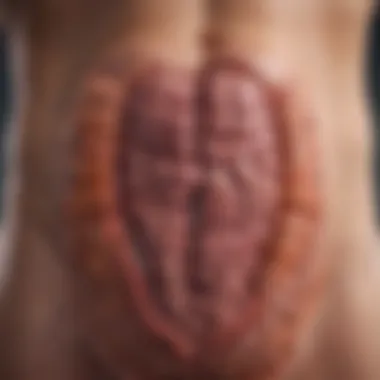
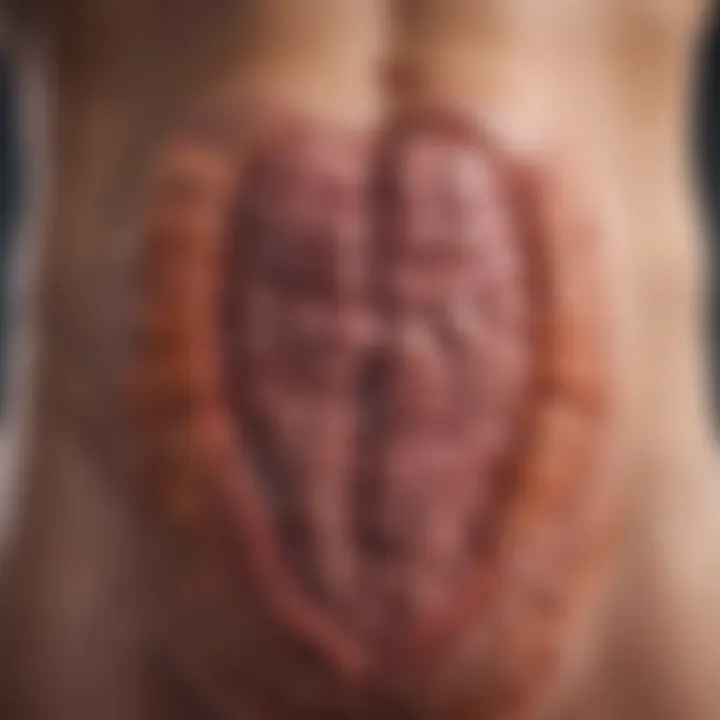
Colectomy
Colectomy is often considered a standard procedure for those with ulcerative colitis. This surgery involves the removal of the colon, which can be beneficial in cases where medical management has failed or severe complications are at hand.
- Key Characteristic: The colectomy can be total or partial, depending on the extent of disease involvement. It allows for the immediate removal of inflamed tissue, reducing symptoms significantly.
- Benefits: Many patients experience a remarkable improvement in their quality of life post-surgery. They often report fewer symptoms or complete relief from the disease, free from the daily management struggles of ulcerative colitis.
- Disadvantages: However, the procedure is not without its challenges. The loss of the colon changes the body’s normal digestive processes, leading to possible complications such as short bowel syndrome or need for an ostomy bag.
Ileal Pouch-Anal Anastomosis
Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) is another advanced surgical option, often utilized after a colectomy. This procedure constructs a pouch from the ileum and connects it to the anal canal, providing patients with a way to eliminate waste without a permanent ostomy.
- Key Characteristic: IPAA preserves the anal sphincter, making it appealing for many since it allows for normal bowel movements instead of relying on an external bag.
- Benefits: Many patients find this procedure to be life-changing, as it allows for improved bowel function and more normality in daily life. It can lead to an enhanced quality of life, especially when compared to a situation involving a permanent ostomy.
- Disadvantages: There can be issues related to pouchitis, which is inflammation of the newly formed pouch, necessitating additional treatment or management strategies.
"Surgical options are not just last-resort measures; they can be life-transforming for many patients struggling against the tide of ulcerative colitis."
"Surgical options are not just last-resort measures; they can be life-transforming for many patients struggling against the tide of ulcerative colitis."
Post-Hospitalization Care
After a stay in the hospital due to ulcerative colitis, post-hospitalization care becomes pivotal for recovery and long-term management. This phase is not just about healing from the immediate illness; it's about setting the stage for a life that minimizes flare-ups and complications. The focus during this period includes developing detailed treatment plans, ensuring continuity of care, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments for better disease management.
The implications of proper post-hospitalization care are vast. It can lead to reduced readmission rates, improved disease control, and an overall enhancement in the patient's quality of life. Each element of this care is intertwined, creating a structured pathway for individuals on their recovery journey.
Continuing Treatment Plans
Medication Adherence
Medication adherence stands out as a central piece of any treatment plan post-hospitalization. This simply refers to the extent to which individuals take their medications as prescribed. A characteristic feature of this adherence is its direct correlation with treatment efficacy. When patients follow their medication schedules diligently, it promotes better control of ulcerative colitis symptoms.
Why is medication adherence considered a beneficial choice? For one, it reduces the likelihood of flare-ups and complications. Patients who adhere to their medication regimens often report fewer severe symptoms, which can significantly enhance day-to-day functioning. Moreover, sticking to medications can prolong remission periods.
However, there’s a unique feature of medication adherence that can’t be overlooked. It requires consistent patient education and motivation. Sometimes, the regimen can be complex, involving multiple medications or strict timing schedules, which can be overwhelming.
Advantages include:
- Reduced symptoms and flare-ups
- Better overall health outcomes
- Enhanced quality of life
Disadvantages can involve:
- Difficulty in understanding complex regimens
- Potential side effects that might discourage adherence
Regular Follow-up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments are equally critical in the post-hospitalization landscape. These appointments serve as checkpoints, providing the medical team an opportunity to evaluate a patient’s progress and adjust treatment plans accordingly. The frequency and nature of these appointments can be tailored to the individual’s needs, which makes it a flexible and beneficial strategy.
The key characteristic of these appointments is the ongoing monitoring of the patient’s condition. They offer a platform for addressing emerging concerns and reinforce the importance of continued care beyond the hospital stay. For many patients, these sessions also act as a motivational tool, reinforcing the commitment to recovery.
A unique aspect of regular follow-up appointments is their adaptability. Based on a patient's status, appointments can vary from monthly check-ins to more frequent visits if deemed necessary.
Advantages of regular follow-ups include:
- Early identification of potential complications
- Adjustments to treatment plans as needed
- Enhanced patient-doctor relationship
Disadvantages can be:
- Time-consuming for patients with busy schedules
- Potential anxiety about appointments for some patients
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are the underlying foundation of effective post-hospitalization care. These changes go beyond just diet; they also encompass stress management, physical activity, and regular health screenings. Adapting to these modifications can be challenging but also enriching in the long run.
For instance, incorporating a balanced diet that minimizes flare-up triggers plays a significant role in managing ulcerative colitis. Patients are encouraged to keep a food diary to pinpoint troublesome foods while promoting the intake of nutrients that support intestinal health.
Moreover, effective stress management techniques—like mindfulness practices or yoga—can ease the mental burden that comes with chronic illness. Regular physical activity, tailored to the individual's ability, fosters both physical and mental well-being.
In summary, navigating post-hospitalization care involves a multifaceted approach that integrates medication adherence, consistent follow-ups, and healthy lifestyle changes. Each piece not only aids in recovery but also empowers patients to reclaim control over their health.
Patient and Caregiver Education
The role of education in managing ulcerative colitis cannot be overstated. Both patients and caregivers must be well-equipped with knowledge to navigate the complexities of this chronic illness. It's like trying to drive a car without understanding how the gears work; without the right information, navigating flare-ups and treatment options can feel overwhelmingly daunting.
Importance of Education
Educating oneself about ulcerative colitis involves grasping the nature of the disease, its symptoms, treatment modalities, and the well-being of both patients and caregivers. Here are key elements to consider:
- Comprehension of the Condition
Understanding that ulcerative colitis is not merely a stomach issue but an autoimmune disorder impacting the colon is pivotal. This understanding establishes the foundation for effective management strategies. - Treatment Options and Plans
Familiarity with medications, like Corticosteroids and Biologics, as well as non-pharmaceutical approaches, helps patients take an active role in managing their condition. Recognizing the specific treatment pathways can demystify the healthcare processes.
Benefits of Educating Patients and Caregivers
Educated patients are empowered patients. They can make informed decisions and engage in discussions with healthcare providers
- Early Detection and Response
With a comprehensive understanding of their symptoms, patients can identify flare-ups sooner and seek help before the condition escalates. This proactive approach can drastically reshape their care trajectory. - Improved Communication
Knowledge allows for better communication between patients and physicians, leading to tailored treatment strategies.
"An educated patient is a partner in care, not just a recipient of services."
"An educated patient is a partner in care, not just a recipient of services."
Considerations in Education
It’s essential to recognize that not everyone learns in the same manner. Tailoring educational approaches to the individual needs of patients and caregivers can make a significant difference. Consider these strategies:
- Use Visual Aids
Diagrams, charts, and videos can simplify complex information and enhance understanding. - Support Groups
Connecting with others facing similar challenges opens doors to shared experiences, creating a sense of community and support for both patients and caregivers. - Resource Accessibility
Utilize credible online resources and literature to provide a well-rounded educational foundation. Websites like Wikipedia and Britannica can be valuable for accurate information.
Through effective education, patients and caregivers can equip themselves with the tools necessary to manage ulcerative colitis and advocate for their health in an informed manner. Understanding day-to-day challenges leads to better coping strategies and enhances overall quality of life.
Recognizing Symptoms of Flare-Ups
A critical aspect of managing ulcerative colitis revolves around understanding the indicators of flare-ups. Recognizing these symptoms early can markedly improve outcomes. Flare-ups can manifest differently, thus, awareness is key. Typically, patients may experience:
- Increased Abdominal Pain
Spikes in discomfort are often the first sign that something is amiss. - Altered Bowel Habits
Changes in stool frequency or consistency, especially if associated with urgency, indicate a potential flare. - Fatigue and Weight Loss
Unexplained tiredness or loss of appetite can signal a downturn in health.
Caregivers should also play an active role in this recognition process. Noting behavioral changes or physical symptoms in the individual they care for can provide critical insights. It's essential for both parties to maintain open lines of communication about any emerging symptoms.
Understanding how these symptoms evolve allows for timely interventions and adjustments in treatment strategies. Recognizing the early signs of an impending flare-up can drastically reduce the risk of hospitalization and encourage continued independence in managing ulcerative colitis.
Quality of Life Considerations
Understanding how ulcerative colitis influences an individual’s overall quality of life is crucial. This chronic condition does not merely affect physical wellness; it casts a wide net over emotional, social, and psychological dimensions too. Hospitalization can alter daily routines, affect relationships, and invoke feelings of uncertainty and vulnerability. These struggles underscore the importance of examining quality of life considerations in the context of ulcerative colitis admissions.
Patient experience is intertwined with various factors, and those experiencing flare-ups often battle a multitude of challenges. Here are some specific elements that highlight the influence of this illness on quality of life:
- Physical limitations: Symptoms like diarrhea and abdominal pain can lead to significant disruptions in daily activities.
- Emotional toll: The unpredictability of the disease may generate anxiety or depression among patients.
- Social isolation: Many patients may find it hard to participate in social gatherings, leading to feelings of loneliness.
- Financial burden: Ongoing medical treatments and possible loss of work can contribute to stress and anxiety.
While it’s essential to manage the physical symptoms of ulcerative colitis, understanding these impacts encourages a more holistic approach to patient care. To foster a supportive environment, tackling these issues head-on can help improve overall well-being.
Psychosocial Impact
The psychosocial impact of ulcerative colitis can reach far and wide. The constant back-and-forth between flare-ups can result in heightened emotions ranging from frustration to despair. For many patients, uncertainty about their health can lead to chronic stress, complicating both daily life and recovery.
Several specific aspects contribute to the psychosocial burden of this disease:
- Fear of hospital stays: The need for hospitalization often arises suddenly, leading to anxiety about what the future may hold.
- Changes in self-image: Physical symptoms, or the side effects from treatments, can alter how individuals see themselves, potentially leading to body image issues.
- Relationships: Intimately tied to emotional states, relationships with family and friends may suffer as patients withdraw or feel misunderstood during their struggle.
- Coping mechanisms: Many patients turn to unhealthy coping strategies, such as avoidance or substance use, which may lead to further complications.
Acknowledging the tremendous psychosocial impact opens avenues for interventions that address mental health as well as physical health. Supportive therapy and counseling resources can greatly assist in managing these psychological challenges, offering effective coping strategies tailored to individual patient needs.
Support Systems
Establishing solid support systems is paramount for anyone coping with ulcerative colitis. The contribution of friends, family, and healthcare professionals can dramatically shift a patient’s experience of the disease. A reliable network can mitigate the emotional challenges faced when navigating life’s demands while dealing with a chronic health issue.
Here are some ways support systems can help:
- Emotional backing: Understanding friends and family can provide critical emotional support, helping patients feel less isolated.
- Practical assistance: Help with daily tasks during flare-ups can alleviate stress, allowing the patient to focus on recovery.
- Educational resources: Connecting with support groups or online communities can equip individuals with practical information and coping strategies from those who share similar experiences.
- Professional guidance: Healthcare professionals offer tailored advice and resources, ensuring patients are well-informed about their condition and treatment options.
Ultimately, empowering patients through strong support systems can facilitate resilience and contribute significantly to their overall well-being.
"Quality of life isn’t just about physical health, it’s a broader picture of emotional, social, and spiritual health as well."
"Quality of life isn’t just about physical health, it’s a broader picture of emotional, social, and spiritual health as well."
Developing strong relationships and resource networks strengthens paths to recovery and eases the transition during challenging times. Ensuring that patients do not feel alone in their journey can create a profound impact on their resilience and hope.
Recent Research and Advances
Recent research in the domain of ulcerative colitis is truly transforming how both patients and healthcare practitioners approach the disease. The implications of these studies are profound, shifting the paradigm toward more effective treatments and improved quality of life for those affected. Understanding these advancements is not just academic; it has real-world consequences for how we manage this chronic condition.
Novel Therapeutic Approaches
There has been a surge in the exploration of novel therapeutic approaches for ulcerative colitis. Notable is the advent of biologic therapies, including monoclonal antibodies such as Infliximab and Adalimumab. Unlike traditional treatments, these biologics specifically target pathways in the inflammatory process, offering a tailored approach to combatting the disease. They have shown promising results in reducing symptoms and promoting remission for many patients who have not responded well to conventional medications.
In addition to biologics, the emergence of small molecules, such as Tofacitinib, brings a new dimension to treatment. This oral medication works by inhibiting specific enzymes involved in the inflammatory process, thus providing a convenient alternative for those who struggle with injections or infusions.
Research is also diversifying into less traditional paths, exploring the gut microbiome's role in ulcerative colitis. Alterations in the gut flora appear to significantly impact the disease's severity and progression. Probiotic therapies are being investigated with the aim of restoring balance in gut bacteria, helping some patients manage their condition more effectively.
"Emerging therapies are not just extending lives; they’re improving the overall living experience for patients battling ulcerative colitis."
"Emerging therapies are not just extending lives; they’re improving the overall living experience for patients battling ulcerative colitis."
Innovations in Patient Care
Innovations in patient care related to ulcerative colitis are equally noteworthy. One major development is the adoption of telehealth consultations. This modality has proven essential, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing patients to access medical advice without the burden of hospital visits. Telehealth has not only increased access but has also made it easier for patients to manage follow-ups and treatment adherence.
Additionally, integrating electronic health records (EHR) with real-time monitoring apps allows healthcare providers to track patient progress more effectively. This capability facilitates immediate intervention should a patient’s condition worsen, which can be a lifesaver during flare-ups.
Nutrition also plays a pivotal role in managing ulcerative colitis. Innovations in personalized nutrition plans, informed by genetic and microbiome data, are gaining traction. It's clear that what works for one patient might not work for another. Thus, tailored dietary strategies can help optimize treatment effectiveness, addressing differing needs based on individual patient profiles.
In summary, the current wave of research and advancements in the treatment of ulcerative colitis showcases a promising future. Both therapeutic innovations and improved patient care methodologies are paving the road toward enhanced management of the disease, ultimately aiming for better health outcomes and a brighter quality of life.
Culmination
In summarizing the complexities surrounding hospitalization due to ulcerative colitis, the conversation leads us to understanding its profound implications for patients and the healthcare system alike. Recognizing ulcerative colitis as more than just a gastrointestinal disorder is critical. This chronic condition not only wreaks havoc on the digestive system but also tremendously affects the patients' quality of life, necessitating periodic admissions to hospitals for acute care or treatment management.
Future Perspectives
As we look ahead, there’s a notable shift towards personalized medicine that may greatly alter the landscape of treatment for ulcerative colitis. Research is shaping new avenues in therapy, focusing on tailored approaches depending on individual patient profiles. We anticipate novel biologic therapies to emerge, aiming to achieve deeper remission and improved life quality. Additionally, technologies such as telemedicine are gaining traction, allowing for innovative follow ups that might include monitoring patients remotely and adjusting treatments based on real-time data. This will bridge significant gaps in healthcare accessibility, making management more effective and responsive.
Summarizing Key Points
- Understanding Hospitalization Triggers: Knowing the reasons behind hospital admissions can guide better prevention strategies. Acute flare-ups and complications should be carefully monitored.
- Effective Management Strategies: In the hospital, the administration of medications like corticosteroids, along with nutritional support, are pivotal in the care journey.
- Surgical Interventions: For some, surgical options like colectomy present a way out of the chronic cycle of flare-ups, necessary for longer-term relief and health.
- Post-Hospitalization Care: Post-discharge, adhering to treatment plans and making necessary lifestyle changes become crucial for maintaining remission and preventing readmission.
In light of these points, the conclusion takes on another layer of complexity. It not just wraps up what’s been discussed, but sheds light on the ongoing developments in ulcerative colitis care and the continuous evolution of best practices. Moreover, fostering awareness and education about this condition can empower patients and caregivers, ultimately leading to better outcomes and improved quality of life for those affected.



