Exploring RA Vasculitis: Insights and Implications


Intro
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is known primarily for its impact on the joints. However, it can often lead to a serious complication that is not widely recognized: vasculitis. This condition can have significant implications, extending beyond the musculoskeletal system to involve various organs, particularly when not identified early. Understanding the complexities of RA vasculitis is essential not only for healthcare professionals but also for patients navigating the challenges of this autoimmune disease.
At its core, RA vasculitis represents an inflammation of the blood vessels that occurs in some individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. This inflammation can result in a wide range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to critical complications. The discussion that follows aims to provide a thorough examination of RA vasculitis, focusing on its pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, and treatment approaches.
Arming both medical practitioners and patients with knowledge is crucial in improving the management of this often-overlooked condition. By a deeper understanding of its mechanics, we can foster better outcomes and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Article Overview
Purpose of the Article
The primary goal of this article is to shine a light on RA vasculitis, exploring it with the detail it requires. The article seeks to inform readers about how this complication arises in the context of rheumatoid arthritis and the potential risks it poses. A thorough examination encourages early recognition and intervention, which can profoundly impact patient care.
Relevance to Multiple Disciplines
RA vasculitis is not a stand-alone concern of rheumatology; it intersects various fields, including:
- Immunology – Understanding the immune response involved in RA and its implications on vasculitis.
- Nephrology – Due to the potential kidney involvement in severe cases.
- Cardiology – As vascular inflammation can affect cardiovascular health.
By exploring the complexities associated with RA vasculitis, this article may promote a collaborative approach among specialists aimed at improving patient outcomes.
Research Background
Historical Context
The study of vasculitis in the realm of rheumatoid arthritis is relatively recent. Historically, systemic implications of rheumatoid arthritis were often overshadowed by joint-related symptoms. Over the past few decades, research has highlighted the significance of systemic manifestations, leading to increased awareness of how RA vasculitis contributes to disease morbidity.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To grasp the nuances of RA vasculitis, understanding a few key concepts is essential:
- Vasculitis refers to the inflammation of blood vessels, leading to issues in blood flow, and potentially affecting multiple organs.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that primarily targets joints but can have systemic effects.
Recognizing these terms sets a solid foundation for unraveling the complexities of RA vasculitis, providing the necessary clarity for further examination.
Preamble to RA Vasculitis
The complexities of autoimmune diseases often leave healthcare providers and patients alike grappling for clarity and understanding. One such condition, RA vasculitis, is an often-misunderstood complication of rheumatoid arthritis. Understanding this condition is vital, as it can have significant implications for patient management and quality of life. It isn’t simply another notch on the belt of rheumatoid arthritis manifestations; RA vasculitis represents a more systemic dilemma that requires keen insight and a tailored approach.
Definition and Overview
To lay the groundwork, RA vasculitis can be defined as a inflammation of the blood vessels that occurs in certain patients with rheumatoid arthritis—a disorder characterized by chronic inflammation primarily affecting joints. The condition may lead to serious complications if silent symptoms are overlooked. The term vasculitis implies an involvement of the vascular system, which could result in anything from skin rashes to more profound nerve damage and organ infarction.
This subset of rheumatoid arthritis is not merely an add-on; its repercussions can spread far and wide through the body, impacting not only physical health but also emotional well-being. For patients and practitioners, understanding the early signs and potential manifestations of RA vasculitis could mean the difference between managing symptoms or confronting dire consequences.
Historical Context
The historical journey of RA vasculitis is as complex as the condition itself. Initially, vasculitis was often misattributed to other causes or disregarded entirely. Prior to the late 20th century, the nuances between various autoimmune disorders and their systemic involvements were not well understood. A few notable strides were made in the late 1980s when the medical community began connecting the dots between rheumatoid arthritis and its vascular implications.
As knowledge burgeoned, case studies emerged in medical literature linking RA with vascular complications. These revelations pointed towards the presence of systemic disease processes that were not merely confined to joint inflammation. Consequently, researchers started to scrutinize how the immune response, which turns the body’s own tissue into a battleground, extends beyond the joints to affect blood vessels.
Such historical explorations underscore the importance of continuous research and education in the field. The better we understand the roots of RA vasculitis—as well as the associated societal and patient challenges—the more equipped we become in addressing not just the symptoms, but also the lived experiences of those affected by it.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Brief Recap
In the realm of autoimmune disorders, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) stands out as a chronic condition with systemic ramifications. It’s crucial to grasp the implications of RA, particularly as it serves as the groundwork for understanding RA vasculitis. This section dives into key aspects that illustrate how RA is not merely a joint ailment but a multifaceted disease that can lead to further complications, including the often-neglected RA vasculitis. A solid comprehension of these foundational elements can better equip healthcare providers as well as patients to navigate the complexities of the condition.
Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis is inherently complex, rooted in an abnormal immune response that targets the body's own synovial lining. The conundrum begins when immune cells, complicating the normal balance, flock to the joints, inflaming the synovial membranes and causing a cascade of inflammatory activities.
- Immune System Dysfunction: The body’s immune system malfunctions, erroneously attacking joint tissues.
- Cytokines and Inflammation: Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-alpha and interleukin-1, perpetuate inflammatory activities, leading to joint erosion and damage.
- Genetic and Environmental Triggers: A mix of genetic predispositions and external triggers, like infections or smoking, contribute to disease onset and progression.
As this cycle of inflammation continues, it can lead not only to joint degradation but also systemic implications, laying the groundwork for complications like RA vasculitis.
Common Symptoms and Progression
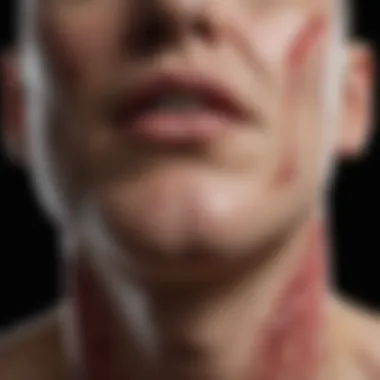

RA presents a range of symptoms that can drastically affect the quality of life for those affected. The hallmark signs include:
- Morning Stiffness: Joint stiffness, particularly in the morning, can last for an hour or more, signaling a flare-up of inflammation.
- Symmetrical Joint Involvement: Asymmetric symptoms are uncommon; typically, if a joint on one side is affected, the same joint on the opposite side also shows symptoms.
- Fatigue and Malaise: Patients often experience a profound sense of fatigue that goes beyond normal tiredness.
Over time, if RA remains unchecked, it can progress to joint deformities and functional impairment. This progressive nature not only complicates daily activities but can also tilt the scales towards more severe manifestations, such as RA vasculitis, marking it as a critical condition for monitoring and prompt intervention.
"Understanding the intricacies of rheumatoid arthritis is pivotal in addressing further complications that may arise, such as RA vasculitis."
"Understanding the intricacies of rheumatoid arthritis is pivotal in addressing further complications that may arise, such as RA vasculitis."
In closing this recap, it's evident that recognizing the implications of rheumatoid arthritis is essential—not only for managing RA but also for being vigilant about its possible complications that can ensue.
The Mechanism of RA Vasculitis
Understanding the mechanism of RA vasculitis is crucial for various reasons. It enhances our grasp of how rheumatoid arthritis can extend beyond joint symptoms to encompass a broader inflammatory response, which can damage blood vessels and lead to systemic complications. The interplay between immune response and inflammation is at the core of this disorder. By delving into this intricate relationship, we can appreciate how RA vasculitis manifests, which will aid in identifying effective treatment strategies and improving overall patient care.
Immune Response and Inflammation
At the heart of RA vasculitis lies a complex immune response that triggers systemic inflammation. Rheumatoid arthritis already sets the stage for an overactive immune system, where the body mistakenly targets its own tissues. When the condition advances to vasculitis, the immune system begins to attack the blood vessels, leading to their inflammation.
This inflammatory response is driven by the presence of autoantibodies and immune complexes, which accumulate and cause local and systemic inflammation. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukins, play a vital role in perpetuating this cycle of inflammation.
The resulting symptoms can include:
- Fever and fatigue: General malaise often accompanies the more pronounced symptoms.
- Skin changes: Rashes or nodules may appear as a result of inflammation.
- Neurological symptoms: When small vessels in the brain are affected, it may lead to atypical headaches or cognitive changes.
Understanding this immune response is not just academically interesting; it translates into clinical practice. Enhanced recognition of how inflammation affects vascular structures allows healthcare providers to predict complications earlier.
By recognizing the signs of immune response in RA vasculitis, timely intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes.
By recognizing the signs of immune response in RA vasculitis, timely intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Impact on Vascular Structures
The consequences of RA vasculitis on vascular structures can be profound and require careful consideration from physicians and patients alike. The inflammation can lead to a number of changes in the vascular system:
- Vasculitis-related complications: Damaged blood vessels can result in ischemia, which might lead to organ damage.
- Aneurysms and thrombosis: Prolonged inflammation can weaken vessel walls, making aneurysms a risk while creating conditions for thrombosis.
- Reduced blood flow: Organs affected by compromised blood flow can suffer; symptoms may manifest as organ dysfunction in severe cases.
The effects on vascular structures can often go unnoticed initially but can worsen over time, leading to serious complications like heart attack or stroke. Thus, greater awareness about how RA vasculitis impacts the vascular system is paramount for timely diagnosis. The interplay between these mechanisms must factor into treatment decisions, helping to tailor individualized management plans for patients suffering from this complex condition.
Clinical Presentation of RA Vasculitis
When delving into RA vasculitis, understanding its clinical presentation becomes a cornerstone in both diagnosis and treatment. The way a patient presents can offer invaluable clues, leading to timely intervention. This section serves to equip healthcare professionals, patients, and their families with essential observations that can significantly alter management strategies and outcomes. Recognizing the signs and symptoms can mean the difference between mild complications and severe consequences.
Common Symptoms and Signs
RA vasculitis can exhibit a myriad of symptoms that may arise suddenly or develop gradually, depending on the extent of involvement and the individual patient. Here are key symptoms that should prompt further examination:
- Skin Manifestations: One of the most telling signs is the development of purpura, which are small purple spots caused by bleeding under the skin. Ulcers may also appear on the extremities, indicating vascular inflammation.
- Joint Pain: While joint discomfort is typical in rheumatoid arthritis, with vasculitis, this pain can intensify and involve other joints unexpectedly, worsening the overall experience.
- Neurological Symptoms: Headaches, dizziness, or even focal neurological deficits can hint at involvement of the central nervous system, marking a serious escalation in symptoms.
- Fatigue and Malaise: Patients may report increased fatigue and a general feeling of unwellness, sometimes described as "running on fumes."
- Systemic Inflammatory Signs: Elevated inflammatory markers in blood tests, like ESR or CRP, alongside unexplained fever, can point towards active vasculitis.
- Renal Symptoms: Hematuria or other renal manifestations may indicate kidney involvement, requiring immediate investigation.
"Timely identification of symptoms is crucial; without it, patients might not receive the care they urgently need."
"Timely identification of symptoms is crucial; without it, patients might not receive the care they urgently need."
Understanding these symptoms allows both practitioners and patients to engage in proactive care, ultimately improving prognosis.
Differential Diagnosis
When faced with potential RA vasculitis presentations, differentiation from other conditions is imperative. Several diseases can mirror these symptoms, making it essential to consider a wide range of possibilities before concluding a diagnosis:
- Infection: Some infections can mimic symptoms of vasculitis, particularly those affecting the skin or nervous system, so rule-outs are necessary.
- Other Types of Vasculitis: Conditions like granulomatosis with polyangiitis or polyarteritis nodosa may present in similar ways but have different management strategies.
- Medication Reactions: Adverse reactions to drugs, notably those used in RA treatment, may cause symptoms akin to vasculitis.
- Malignancies: Certain cancers can present with skin changes or systemic symptoms, requiring careful investigation to exclude them.
Utilizing a structured approach to differential diagnosis can avoid misdiagnosis and ensure that patients receive the most appropriate care. Clinical presentations are just one piece of the puzzle; how these presentations interact with the patient’s overall health picture is key to effective management and therapeutic outcomes.
Diagnostic Approaches
In the realm of RA vasculitis, diagnostic approaches form the bedrock of effective management and treatment strategies. Recognizing this condition early can significantly alter patient outcomes, making these approaches not just relevant but essential. Through targeted assessments—comprising laboratory tests, imaging techniques, and histological examinations—healthcare providers can proficiently identify and delineate the extent of vasculitis in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. This section will delve into each diagnostic method, outlining their importance while highlighting how they weave into the broader narrative of RA vasculitis management.
Laboratory Tests


Laboratory tests serve as the initial touchpoint in diagnosing RA vasculitis. These tests help in evaluating inflammatory markers that can indicate systemic involvement. Key components of laboratory evaluations include the following:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test is integral for identifying anemia or thrombocytopenia, both of which may point towards inflammation or disease activity.
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): This is a non-specific measure, but a high ESR often suggests inflammation. It's not definitive for RA vasculitis but can direct further investigation.
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP): Elevated CRP levels in the blood can indicate acute inflammation, thus giving clinicians a clearer direction regarding the disease's activity level.
- Antibody Testing: Tests for various autoantibodies, such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA), assist in confirming a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, which may be linked to vasculitis.
In performing these tests, there's careful consideration of the patient's overall context. Healthcare providers must keep in mind that lab results should be interpreted in conjunction with clinical symptoms for accurate diagnostics.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging plays a critical role in the assessment of RA vasculitis, particularly in evaluating vascular and soft tissue changes. Various imaging techniques provide insights into the anatomical and functional aspects of affected structures:
- Ultrasonography: Often a first-line imaging modality, it can visualize vascular involvement without the risks associated with other imaging types. It’s non-invasive and readily accessible.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is invaluable for its detailed view of soft tissues and vessels. It can help detect inflammatory changes in the blood vessels and surrounding tissues, aiding in a more comprehensive assessment.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans are particularly useful for evaluating larger vessels and can reveal complications like aneurysms or occlusions that may arise due to vasculitis.
Each of these imaging modalities offers distinct benefits, with their selection largely dependent on the clinical situation at hand. The challenge is in aligning the chosen approaches with the symptoms and potential areas of concern, always mindful that too much radiation exposure from repeated CT scans can be a risk.
Histological Examination
Histological examination, while perhaps less frequently employed, is pivotal when a precise confirmation of RA vasculitis is necessary. This method digs deep at the cellular level to unveil the underlying pathological changes that typify vasculitis:
- Biopsy Specimens: Obtaining biopsy samples from involved tissues—whether from skin, muscle, or larger organs—can provide a direct look at inflammatory changes. This method allows pathologists to identify the specific type of vasculitis, which is essential for tailored treatment plans.
- Immunofluorescence Studies: In conjunction with biopsies, these tests can reveal immune complex deposits in vascular walls, further delineating the autoimmune processes at play.
A well-executed histological examination not only confirms the diagnosis but also enhances understanding of the disease’s behavior, informing therapeutic strategies more accurately.
Management Strategies for RA Vasculitis
Understanding how to effectively manage RA vasculitis is crucial for improving patient outcomes. This condition, a serious complication of rheumatoid arthritis, can lead to significant morbidity if not addressed appropriately. In this section, we will delve into the pharmacological treatments and non-pharmacological approaches that form the backbone of management strategies for RA vasculitis.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological treatments for RA vasculitis aim to mitigate inflammation and suppress the aberrant immune response that drives this condition. These medications are essential in restoring normal function and preventing further vascular damage.
- Corticosteroids:
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs):
- Biologics:
- Pain Management:
- Corticosteroids like prednisone are often the first line of treatment. They provide rapid relief from inflammation and can lead to quick improvements in symptoms. However, long-term use needs careful monitoring due to potential side effects—think about bone density loss!
- DMARDs are used to regulate the immune system and slow disease progression. Methotrexate and azathioprine are common choices. They come with their own set of challenges and require regular lab checks to monitor for toxicity.
- For patients unresponsive to traditional DMARDs, biologic therapies like rituximab and tocilizumab have emerged as game changers. These agents target specific components of the immune system, providing precision therapy that can be life-saving.
- Alongside anti-inflammatory medications, pain management strategies, such as NSAIDs, play an integral role. They help in managing the discomfort that patients experience.
The balancing act in pharmacological treatments revolves around efficacy and safety. While medications are key to controlling symptoms and preventing complications, their side effects demand a targeted and individualized approach to therapy. Collaborating with the healthcare team is vital for optimizing treatment plans.
Non-Pharmacological Approaches
Beyond medications, various non-pharmacological approaches can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals with RA vasculitis. They complement medical therapies and support holistic management.
- Physical therapy:
- Dietary modifications:
- Stress management:
- Engaging in tailored physical therapy can help maintain joint function and reduce stiffness. Therapists often incorporate stretching, strengthening exercises, and hydrotherapy into their plans for rehabilitative benefits.
- Nutrition plays a pivotal role in managing inflammation. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids—found in fish and flaxseed—along with fruits and vegetables can have a anti-inflammatory effect. It's also wise to limit processed foods and sugars to maintain overall health.
- Stress can amplify symptoms, hence incorporating mindfulness practices, such as yoga or meditation, may improve overall well-being. Support groups can also be beneficial, offering a platform to share experiences and coping strategies with others in similar situations.
In summary, effective management of RA vasculitis requires a comprehensive approach that blends pharmacological treatments and non-pharmacological strategies. This ensures better control of the disease and enhances the quality of life for those affected. Aligning treatment goals among patients, families, and healthcare providers is imperative for achieving successful outcomes.
Early and comprehensive management of RA vasculitis is not merely a treatment plan—it’s a lifeline for many, aiming to restore health and improve the quality of life.
Early and comprehensive management of RA vasculitis is not merely a treatment plan—it’s a lifeline for many, aiming to restore health and improve the quality of life.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes
Understanding the prognosis and long-term outcomes of RA vasculitis is a critical aspect of managing this complex condition. For healthcare providers and patients alike, grasping the potential trajectory of the disease can make all the difference in treatment planning and quality of life. Prognosis is influenced by numerous factors that can vary widely among individuals. These factors must be considered when developing a personalized care plan that targets the patient's specific needs.
Factors Influencing Prognosis


Several key elements impact the prognosis of RA vasculitis. Identifying them early allows for better intervention strategies:
- Disease Severity: The initial severity of rheumatoid arthritis tends to correlate with the progression of RA vasculitis. A severe pre-existing condition may indicate a higher risk of complications.
- Duration of Symptoms: The length of time a patient experiences symptoms before diagnosis can affect outcomes. Early recognition often leads to better management strategies.
- Treatment Response: How well a patient responds to therapies, both pharmacological and non-pharmacological, significantly shapes prognosis. If a patient demonstrates a robust response to treatment, it often points to a more favorable long-term outcome.
- Comorbid Conditions: Other underlying health issues can complicate the situation. Conditions like diabetes or cardiovascular diseases may exacerbate the prognosis of RA vasculitis.
- Age and Gender: Studies suggest that age plays a role in disease progression, with older adults often facing poorer outcomes. Additionally, some trends indicate that women may have different experiences compared to men in terms of disease severity.
"The prognosis of RA Vasculitis is like a fork in the road, where choices made can deeply influence the direction and quality of life ahead."
"The prognosis of RA Vasculitis is like a fork in the road, where choices made can deeply influence the direction and quality of life ahead."
Complications Associated with RA Vasculitis
Complications arising from RA vasculitis can vastly affect the long-term health of patients. Being aware of these potential issues promotes proactive management:
- Vascular Complications: RA vasculitis can lead to serious vascular problems, including aneurysms and thrombosis, that can have severe consequences if not monitored.
- Kidney Damage: One of the more severe complications involves renal issues since inflammation can affect the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to renal failure.
- Neurological Issues: In rare instances, vasculitis can impact the central nervous system, causing symptoms such as headaches, seizures, or even cognitive impairments.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Patients undergoing immunosuppressive therapies might also face a higher risk of infections, complicating their health situation.
- Chronic Pain and Fatigue: Many patients report ongoing pain and fatigue, which can significantly impair daily living and psychosocial wellbeing.
Ultimately, understanding the prognosis and possible long-term outcomes of RA vasculitis aids in setting realistic expectations and promotes a collaborative environment between doctors and patients. By staying informed, patients can take an active role in their care, leading to more meaningful and effective treatment strategies.
Recent Research and Developments
Recent advancements in the understanding and treatment of RA vasculitis hold significant promise for those affected by this complex complication. Research plays an integral role in shaping clinical practices, informing guidelines, and enhancing patient care strategies. Moreover, ongoing studies contribute to a more profound comprehension of the disease’s mechanism and progression, which can lead to improved outcomes. As we delve into the emerging therapies and innovations in diagnostic techniques, we witness a landscape evolving rapidly, offering new hope and insights.
Emerging Therapies
Emerging therapies for RA vasculitis are pivotal in improving patient management. With biologic drugs at the forefront, treatments target specific pathways in the immune response, thereby reducing inflammation and preventing further vascular damage. The use of agents like tocilizumab, which blocks interleukin-6, has shown promise in clinical settings, allowing a tailored approach to each patient’s unique challenges.
Recent studies have explored novel compounds as well. For instance, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors like filgotinib and baricitinib, which interfere with signaling in immune cells, have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing symptoms and disease activity. The key benefits of these emerging therapies are:
- Precision Targeting: More effective treatments that consider individual differences in disease expression.
- Reduced Side Effects: Targeted therapies often lead to fewer systemic side effects compared to traditional medications.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients often experience significant improvements in their everyday activities and general well-being.
While these advancements are encouraging, careful consideration and robust clinical trials are essential to ensure their safety and long-term effectiveness.
Innovations in Diagnostic Techniques
Innovations in diagnostic techniques are equally critical in understanding and addressing RA vasculitis effectively. As the old adage goes, "A stitch in time saves nine," and recognizing the condition early can significantly enhance treatment efficacy. Advanced imaging technologies such as high-resolution ultrasounds and magnetic resonance angiography are coming to the forefront, allowing clinicians to visualize vascular changes with greater clarity. This not only aids in diagnosis but also facilitates monitoring of disease progression and treatment response.
Among the recent advancements, the use of biomarkers to detect inflammatory processes is gaining traction. For example, studies are investigating the utility of various serum cytokines and acute phase reactants as indicators of vasculitis activity. These innovations provide:
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: Getting to the root of the issue quickly is paramount.
- Tailored Treatment Approaches: Allows for treatment adjustments based on real-time feedback.
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Understanding the full scope of the disease can lead to better planning for complications.
By integrating these novel diagnostic techniques into clinical workflows, healthcare providers can greatly improve patient outcomes, thus underscoring the importance of recent research in this area. As we see developments unfold, it is essential to stay informed and adaptable in our approaches to care.
Patient Care and Support
The multifaceted nature of RA vasculitis demands not just clinical intervention but also a robust system of patient care and support. As patients grapple with this often-overlooked complication of rheumatoid arthritis, the role of healthcare professionals evolves beyond the confines of medical treatment to encompass education, emotional support, and lifestyle management. An effective support system ensures that patients are not merely passive recipients of care but active participants in their healing journey.
Educating Patients About RA Vasculitis
Effective education serves as the backbone for understanding RA vasculitis. Patients often feel overwhelmed when faced with a diagnosis that intertwines complex symptoms and treatment protocols. Hence, ensuring they grasp the condition's nuances is crucial.
- Simplified Communication: Use layman's terms when explaining medical jargon. For instance, while discussing the autoimmune nature of RA vasculitis, phrases like "the body gets confused and starts attacking itself" can resonate better than clinical definitions.
- Resources and Materials: Providing brochures or links to reputable online resources, such as articles from britannica.com or community discussions on platforms like reddit.com, can encourage self-education. Patients should be empowered to research and understand their condition further.
- Ongoing Dialogue: Implement regular check-ins or workshops that focus on RA vasculitis. Facilitating open discussions about challenges, treatment side-effects, or even simply sharing experiences can greatly enhance the patient's understanding and confidence.
Psychosocial Considerations
In addition to the clinical aspects, the psychosocial dimensions of living with RA vasculitis need careful attention. The emotional toll of chronic disease can be profound, leading many patients to face feelings of isolation or despair. Recognizing and addressing these concerns can significantly enhance overall well-being.
- Support Groups: Encourage participation in community support groups. Interaction with peers who've had similar experiences can provide a sense of belonging and understanding.
- Mental Health: Regular screenings for depression or anxiety should be standard. Mental health interferes not just with emotional well-being but often impacts adherence to treatment plans.
- Family Involvement: Involving family members in education sessions can foster a supportive home environment. It’s imperative that families understand the condition to provide comfort and assistance to their loved ones.
"Educating oneself about the illness is not solely about understanding it; it's also about regaining control over one's life."
"Educating oneself about the illness is not solely about understanding it; it's also about regaining control over one's life."
Through a holistic approach combining patient education and psychosocial support, healthcare providers can cultivate a therapeutic environment that respects the complexities of RA vasculitis. This multifaceted strategy not only equips patients with knowledge but also the emotional backbone essential for effectively navigating their healthcare journey.
Closure
As we draw our examination of RA vasculitis to a close, it becomes abundantly clear that understanding this condition is not just a medical necessity but a cornerstone for improving patient outcomes. RA vasculitis, often underestimated, spirals from the complexities of rheumatoid arthritis, altering the landscape of how we perceive autoimmune diseases.
Summary of Key Insights
In the previous sections, we navigated through the intricate web of mechanisms and clinical presentations particular to RA vasculitis. The key insights gathered are paramount in grasping its significance:
- Pathophysiology: An intricate interplay between immune dysregulation and inflammation catalyzes the progression of RA vasculitis. Awareness of these processes can aid in quicker diagnoses.
- Clinical Manifestations: Symptoms vary widely but can lead to severe organ damage if left unchecked. Recognizing these early indicators fosters timely treatment decisions.
- Diagnostics and Management: The fusion of robust diagnostic tools and innovative treatment strategies is critical. As healthcare professionals, staying abreast of these advancements can transform the approach to care
Future Directions in Research
Looking ahead, the field must prioritize the exploration of several pivotal areas:
- Understanding Genetic Factors: Further studies are needed to illuminate how genetics might predispose individuals to RA vasculitis and influence the disease's severity.
- Innovative Therapeutic Strategies: Ongoing research should focus on harnessing biologics and targeted therapies that may offer enhanced efficacy with fewer side effects.
- Longitudinal Studies: Understanding the long-term effects of RA vasculitis and its impact on quality of life can inform better management strategies.
In essence, as we continue to peel back the layers of RA vasculitis, it is critical for both researchers and practitioners to engage in a continuous dialogue. This collaboration will not only extend our comprehension but enhance the support provided to patients grappling with this multifaceted condition. In a world where information and research are rapidly evolving, staying informed is key to fostering an environment of proactive care and hope for those affected.



