In-Depth Insights on Neurofibromatosis Type One


Intro
Neurofibromatosis Type One (NF1) presents a labyrinth of challenges, often span across various aspects of human health. This genetic disorder, which manifests through benign tumors, particularly along the nerves, affects not just the physical well-being of individuals but also carries psychological and social implications. The nuanced nature of this condition calls for an in-depth exploration that intertwines medical understanding with practical application.
By scrutinizing NF1, we can glean insights that extend beyond the mere clinical descriptions; it offers a window into the intricate interplay of genetics, pathology, and patient care. The insights gleaned from this examination could equally enlighten health practitioners, researchers, and those directly impacted.
Article Overview
Purpose of the Article
The purpose of our exploration into NF1 is manifold. It aims to:
- Provide a thorough understanding of NF1’s pathophysiology.
- Illuminate the clinical manifestations and the diagnostic processes involved.
- Discuss therapeutic strategies that hold promise for management.
- Emphasize the urgent need for early detection and customized treatment approaches.
Relevance to Multiple Disciplines
This article stands at the intersection of various disciplines. It holds significance for:
- Medical professionals, who must recognize the signs and symptoms early.
- Researchers, exploring the genetic underpinnings and potential treatments.
- Educators, aiming to impart knowledge about NF1 in instructional settings.
- Families and affected individuals, who seek insight into what NF1 entails and how to navigate it.
As a genetic disorder, NF1 does not merely belong to the realm of genetics; its implications stretch into clinical practice, educational curriculums, and patient support frameworks.
Research Background
Historical Context
The understanding of Neurofibromatosis Type One has evolved significantly since its initial documentation. First recognized in the early 19th century by researchers like Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen, who linked skin tumors to nerve tissue, NF1 has undergone an extensive journey of exploration. From its ornamental beginnings in medical literature to the detailed genetic mapping we see today, this history reveals much about the progress in genetics and neurology.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To ground our exploration, we must clarify some fundamental concepts:
- Tumors: NF1 is characterized by the development of neurofibromas, which are benign tumors that can arise in various locations within the body.
- Café au lait spots: These are light brown skin patches often observed in NF1 patients and serve as one of the diagnostic criteria.
- Genetic Mutation: NF1 is caused by mutations in the NF1 gene, disrupting the production of neurofibromin, a protein that helps regulate cell growth.
Understanding these terms is integral to fully grasping the complexities that NF1 entails.
"Understanding NF1 requires not just a grasp of the medical facts, but a sensitivity to the voices of those impacted by the disorder."
"Understanding NF1 requires not just a grasp of the medical facts, but a sensitivity to the voices of those impacted by the disorder."
Through this deep dive into NF1, it is hoped that we cultivate a clearer comprehension of this condition, bridging the gap between academic inquiry and real-world experiences.
Preamble to Neurofibromatosis Type One
Neurofibromatosis Type One (NF1) is not just another genetic condition; it’s a multifaceted disorder that requires a nuanced understanding to navigate its complexities. Those grappling with NF1 encounter a spectrum of challenges that vary greatly from one individual to another.
Definition and Historical Context
Neurofibromatosis Type One can be defined as a genetic disorder marked primarily by the growth of benign tumors along nerves, known as neurofibromas. The foggy history of NF1 stretches back over a century, with its first descriptions appearing in medical literature in the 1880s. The name 'neurofibromatosis' itself hints at the nature of the disorder: roots in both the nervous system and fibrous tissue. Historically, cases were often shuffled under the carpet of general tumor pathology until meticulous researchers began to draw connections, recognizing the unique patterns of symptomatology that characterize NF1. One of the early pioneers in this field, Dr. Friedrich von Recklinghausen, published observations that not only helped establish NF1 as a distinct entity but also laid the groundwork for future research.
Epidemiology and Prevalence
Epidemiologically speaking, NF1 is more prevalent than one might assume. It affects roughly 1 in every 3,000 individuals globally. Surprisingly, NF1 has no preference for gender or ethnicity. This means that anyone could find themselves on this unexpected journey. The diagnosis often comes as a shock to many families, particularly if there is no known family history of the disorder. Current data suggests that approximately half of the cases arise from a spontaneous mutation rather than inheritance. The nuances of how NF1 presents can vary greatly from one person to another, ranging from mild manifestations that resemble freckles to more severe complications that impact the quality of life. Additionally, ongoing studies strive to provide richer datasets, delving deeper into the socio-economic factors that can affect the quality of healthcare and life for those living with NF1.
"Understanding the epidemiology of NF1 is crucial for recognizing affected individuals early and implementing early interventions, which may significantly improve patient outcomes."
"Understanding the epidemiology of NF1 is crucial for recognizing affected individuals early and implementing early interventions, which may significantly improve patient outcomes."
Genetic Basis of NF1
Understanding the genetic basis of Neurofibromatosis Type One (NF1) is fundamental in comprehending how this condition manifests and evolves within individuals. Genetic insights not only illuminate the underlying mechanisms that lead to NF1, but they also offer pathways to better management and potential therapies.
The NF1 gene functions primarily to produce a protein known as neurofibromin, which plays a crucial role in regulating cell growth. Deficiencies in this protein can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation, giving rise to the tumors characteristic of NF1.
NF1 Gene and Its Functions
The NF1 gene is located on chromosome 17, and its complete sequence provides important clues about its functionality. As a tumor suppressor gene, it acts as a control mechanism for cell division and growth. In individuals with NF1, mutations in the NF1 gene can lead to a loss of neurofibromin function, allowing cells to multiply uncontrollably. This malfunction contributes to the formation of neurofibromas—benign tumors that arise from the nerve sheath—as well as other complications associated with the disorder.
Neurofibromin serves various roles, including the modulation of signaling pathways important for cellular processes. Its absence or dysfunction may also disrupt the pathway involving RAS protein, which is pivotal in important functions like growth and division. Understanding the gene’s role illuminates the broader landscape of tumorigenesis in NF1, effectively connecting genetic abnormalities to clinical presentations.


Inheritance Patterns
Neurofibromatosis Type One follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. This means that only one copy of the altered gene, inherited from an affected parent, is sufficient to cause the disorder. Each child of an affected parent has a 50% chance of inheriting the mutation. However, it’s also noteworthy that about 30% of NF1 cases arise from spontaneous mutations, indicating that not all individuals with NF1 have a family history of the condition.
The variability in the manifestation of NF1 also ties back to the gene’s characteristics. Some individuals may show severe symptoms while others might experience mild or even asymptomatic cases. This variability stems from factors such as the specific mutation of the NF1 gene and how it interacts with environmental elements.
Genetic Testing and Counseling
Genetic testing can offer vital information for families with a history of NF1 or for individuals suspected of having the disorder. Through such testing, healthcare providers can confirm or rule out the presence of mutations in the NF1 gene, facilitating early detection and monitoring of the disease.
Genetic counseling plays a critical role alongside genetic testing. Counselors can guide families about the implications of testing results, discussing the likelihood of passing the condition to offspring. They can help individuals navigate decisions regarding family planning, emphasizing the importance of a tailored approach based on personal and familial circumstances.
"Genetic understanding is not just about chromosomes and mutations; it’s about informing choices and improving lives."
"Genetic understanding is not just about chromosomes and mutations; it’s about informing choices and improving lives."
In summary, the genetic basis of Neurofibromatosis Type One is a pivotal aspect that intertwines with clinical features, management strategies, and emotional wellbeing. Through a solid grasp of the NF1 gene functions, inheritance patterns, and the power of genetic testing, we can better comprehend both the complexities and the support applicable to those affected by NF1.
Clinical Features of NF1
Understanding the clinical features of Neurofibromatosis Type One (NF1) is crucial for both diagnosis and management of this complex disorder. Patients with NF1 present a wide range of symptoms that can vary significantly in severity and manifestation. Recognizing these features early on can help in tailoring treatment strategies and enhancing the quality of life for those affected. The clinical features not only assist in diagnosing the condition but also provide insights into potential comorbidities and complications that may arise over time.
Characteristic Skin Manifestations
One of the hallmark signs of NF1 are the skin manifestations, which include multiple neurofibromas, café-au-lait spots, and axillary freckling. Neurofibromas are benign tumors that can appear anywhere along the body but are often found on the trunk, head, or extremities. While they can be small and asymptomatic, larger neurofibromas may cause discomfort or emotional distress due to their appearance. This variability highlights the importance of ongoing skin assessments to monitor changes or growth in these tumors.
Café-au-lait spots are flat, pigmented marks on the skin. Their presence, especially when exceeding six spots larger than 5 millimeters in diameter, can be a key diagnostic indicator of NF1. The axillary freckling, which may occur in the armpits and groin area, is another clinical clue, giving practitioners a visual cue during examinations. This collection of skin features suggests a need for dermatological evaluation free from superfluous diagnostic procedures, making it vital for patients to understand their significance.
Nervous System Involvement
The implications of NF1 extend beyond the skin. Nervous system involvement is a significant aspect of NF1 that can lead to various neurological challenges. Tumors can develop along peripheral nerves, leading to conditions like pain, sensory loss, or weakness. These tumors may also infiltrate the spinal cord or brain, generating complications such as learning disabilities, attention disorders, or even more severe neurological deficits.
Moreover, the involvement of the optic nerve, known as optic pathway gliomas, poses a notable risk. These tumors can lead to vision impairment or loss, emphasizing the critical need for regular ophthalmologic exams. Given these potential impacts, early detection of neurologic manifestations through careful monitoring and the use of advanced imaging modalities can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Associated Comorbidities
Living with NF1 often comes hand-in-hand with a host of associated comorbidities. Patients are at increased risk for skeletal issues, including scoliosis and tibial dysplasia. These structural abnormalities can lead to mobility issues or chronic pain, necessitating multidisciplinary care that encompasses both orthopedic and neurologic assessments.
Other comorbidities can be psychological, such as increased rates of anxiety or depression, which is often exacerbated by the visible aspects of the condition and the unpredictability of its clinical course. Educational struggles may arise, particularly for children, making tailored support programs in schools essential.
Given this intertwining of physical and psychological factors, a targeted approach involving medical professionals, educators, and mental health resources is paramount. By addressing both physical and emotional health, we can help improve the overall well-being and functionality of those living with NF1.
"Early identification and appropriate interventions are crucial in managing the multifaceted challenges faced by individuals with NF1."
"Early identification and appropriate interventions are crucial in managing the multifaceted challenges faced by individuals with NF1."
In summary, recognizing the clinical features of NF1 is vital not just for diagnosis but for shaping personalized management strategies that encompass the unique challenges inherent in this condition. By fostering a holistic approach, healthcare providers can help patients navigate their journey with greater ease and support.
Diagnostic Approaches
The evaluation and diagnosis of Neurofibromatosis Type One (NF1) present both challenges and opportunities for healthcare professionals. Understanding the importance of effective diagnostic strategies is key to managing this complex condition. Early diagnosis can significantly improve clinical outcomes, as it enables timely interventions and informed care plans for patients. Consistent and accurate application of diagnostic criteria can prevent misdiagnoses that ultimately lead to ineffective treatment strategies or unnecessary anxiety for patients and their families.
Clinical Evaluation and Criteria
Clinical evaluation forms the bedrock of diagnosing NF1. Physicians typically begin with a thorough patient history and a comprehensive physical examination. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) criteria, which are widely accepted in the medical community, the diagnosis of NF1 can often be made when an individual meets at least two of the following six criteria:
- Six or more cafe-au-lait spots, each measuring 5 mm or more in diameter in prepubertal individuals or 15 mm or more in diameter in postpubertal individuals.
- Two or more neurofibromas of any type or one plexiform neurofibroma.
- Freckling in the axillary or inguinal regions.
- Optical glioma.
- Two or more Lisch nodules (iris hamartomas).
- A first-degree relative with NF1 (i.e., parent, sibling, or child).
This approach often allows for a diagnosis to be made at an early age, sometimes as young as two years old. For many families, receiving a definitive diagnosis of NF1 provides a sense of clarity, albeit accompanied sometimes by concerns about the implications of the disorder.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques are critical for further assessing the extent of NF1 manifestations. Imaging helps visualize underlying neurofibromas that may not be apparent during a physical exam. The following modalities are commonly employed:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This is the go-to method for documenting the presence of neurofibromas, especially in deeper tissues and the central nervous system. Because MRIs can provide detailed images of soft tissue, they are instrumental in monitoring plexiform neurofibromas and possible complications, such as malignancy.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Though not the primary imaging technique for NF1, CT scans can also provide valuable insights, particularly when MRI is unavailable. They are often used for assessing bony lesions and other complications.
Utilizing imaging techniques as a part of the diagnostic toolkit allows healthcare providers to holistically evaluate a patient’s condition, thereby informing treatment decisions more effectively.
Differential Diagnosis
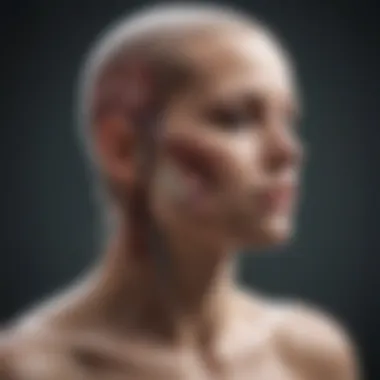

Differentiating NF1 from other similar conditions can be perplexing due to overlapping clinical features. Other genetic syndromes, such as Neurofibromatosis Type Two, von Hippel–Lindau disease, or schwannomatosis, may present with symptoms that can mimic NF1. Here are critical aspects to consider during differential diagnosis:
- Phenotypic Variability: NF1 can exhibit a wide range of presentations, from mild cutaneous features to significant neurological involvement, leading to potential confusion with similar syndromes.
- Genetic Testing: When clinical evaluation is inconclusive, genetic testing for mutations in the NF1 gene can confirm a diagnosis. This provides a clearer path for patient management and genetic counseling.
- Family History: Taking a thorough family history can often help delineate whether a case is likely NF1 or another condition. Many families carry a gene that connects various diagnoses, and understanding this familial link is vital.
Being diligent in making a differential diagnosis not only serves the clinical community well but also ensures that the patient's journey is directed with precision and care, ultimately aiming to improve quality of life outcomes.
"An accurate diagnosis of NF1 makes the journey easier for both patients and healthcare providers, catalyzing effective management strategies that consider the whole person, not just the disorder."
"An accurate diagnosis of NF1 makes the journey easier for both patients and healthcare providers, catalyzing effective management strategies that consider the whole person, not just the disorder."
By employing these diverse diagnostic approaches, healthcare providers can significantly enhance the quality of care for patients with NF1, enabling early intervention and comprehensive management plans.
Management and Treatment Strategies
In addressing Neurofibromatosis Type One, the topic of management and treatment strategies maters a lot. It not only sheds light on how to handle the symptoms and complications of NF1 but also emphasizes the necessity of an organized and multifaceted approach. Individuals dealing with NF1 come with unique needs and challenges, making it essential for healthcare providers to tailor strategies that cater to each individual. The effectiveness of treatments, the involvement of various specialties, and their collaborative efforts ultimately contribute to better outcomes for those affected.
Multidisciplinary Care Approaches
When managing NF1, a multidisciplinary care approach is vital. This method involves a team of professionals from different specialties working together to address various aspects of the disorder. Doctors focusing on genetics, dermatology, neurology, and oncology, for instance, can collaborate to provide comprehensive care. Utilizing diverse expertise ensures that no stone is left unturned in monitoring the patient’s overall health.
By pooling resources, a deeper understanding of the patient’s situation emerges. For instance:
- Geneticists can offer insights into the hereditary factors, aiding in targeted counseling.
- Dermatologists handle skin manifestations, ensuring prompt treatment for lesions and other related concerns.
- Neurologists monitor and manage neurological symptoms and potential complications.
This approach mitigates gaps often found in healthcare systems where specialization can lead to fragmented care. Patients benefit by receiving coordinated follow-ups, reducing unnecessary repetitions and confusion. When these experts share information, treatment plans become more robust and holistic, increasing the likelihood of positive outcomes.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery might be necessary for patients with NF1, especially when tumors or other growths cause discomfort or put pressure on nerves. Surgical interventions focus on removal of neurofibromas and, when beneficial, the alleviation of complications caused by those tumors. It's not as simple as just cutting them out; the complexity lies in assessing when surgical interventions offer more benefit than risk.
Some common considerations include:
- Histopathological Evaluation: Prior to surgery, biopsies or imaging can help ascertain the type of tumor and associated risks.
- Patient’s Quality of Life: The decision to operate often hinges on how significantly NF1 impacts the daily life of the individual.
- Disease Progression Monitoring: Surgical options should be revisited as NF1 evolves, aligning with the ongoing monitoring regime.
Ultimately, surgical procedures should be employed judiciously and as a part of a broader management plan tailored for the individual.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological treatments aim to alleviate symptoms and manage complications arising from NF1. While there's no cure for the disorder itself, medications can frequently make the living experience smoother for the ones affected. Commonly, practitioners might prescribe:
- Pain Management Drugs: For those with persistent pain due to tumor growth.
- Beta-Blockers: Sometimes used to control symptoms stemming from secondary complications, such as blood pressure issues.
- Targeted Therapies: Newer drugs are in development that may specifically target the pathways involved in tumor growth through ongoing research efforts.
Pharmacological approaches highlight the importance of customizing treatment to fit patient needs, adjusting dosages or switching medications based on response and tolerance. Communication with healthcare providers remains crucial, ensuring that patients understand their medication plans and can report any side effects promptly.
Psychosocial Support
Living with NF1 often brings about emotional and psychological challenges, making psychosocial support an integral part of comprehensive care. Conditions like anxiety, depression, and social isolation can often be found in individuals with NF1, necessitating support from mental health professionals. Here are key elements that should be incorporated:
- Counseling Services: Regular sessions with a psychologist can provide emotional relief and coping strategies for affected individuals and their families.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others experiencing similar challenges offers insight and solidarity, easing the feeling of isolation.
- Parental Guidance: For children diagnosed with NF1, providing parents with resources on how to best navigate the educational system for support can significantly impact the child’s development and self-esteem.
"Holistic care goes beyond treating symptoms; it's about nurturing the entire individual, mental health included."
"Holistic care goes beyond treating symptoms; it's about nurturing the entire individual, mental health included."
In summary, a successful management plan requires diverse strategies employed in sync. It’s not just about the medical aspect; understanding a patient's emotional and mental state is equally important in the quest for effective treatment. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, a comprehensive approach stands as a beacon of hope for those navigating the challenges associated with Neurofibromatosis Type One.
Research Advances and Future Directions
The field of neurofibromatosis type one (NF1) research is rapidly evolving, shedding light on the condition and improving management strategies. With a complex genetic backdrop, understanding these advances is crucial for professionals and researchers focusing on better outcomes for those affected.
Emerging Therapies
In recent years, the quest for effective treatments has driven researchers to explore various emerging therapies for NF1. One notable area is the development of targeted therapies that aim to specifically attack tumor cells associated with NF1.
- MEK Inhibitors: Drugs such as trametinib have shown promise. They inhibit the MEK pathway, which is often hyperactivated in the tumors of NF1 patients. Early trials suggest that these treatments can significantly reduce tumor size and improve patient outcomes, showing that targeting specific molecular pathways might provide effective management tools.
- Gene Therapy Approaches: Emerging techniques involving gene editing, such as CRISPR, offer a forward-thinking avenue. This innovative method allows scientists to make precise changes to the DNA, potentially correcting mutations in the NF1 gene itself. While current studies are preliminary, the future of these therapies holds promise for fundamentally altering the disease’s course.
Current Clinical Trials


Clinical trials are the backbone of therapeutic advancement, helping to establish the efficacy and safety of new treatments. A variety of ongoing trials focus on both pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical interventions:
"Clinical trials not only probe new treatments but enrich our understanding of NF1 itself."
"Clinical trials not only probe new treatments but enrich our understanding of NF1 itself."
- Randomized Trials: Some trials assess the effectiveness of combination therapies, integrating both pharmacological and experimental medical approaches. This includes testing novel drugs alongside established treatments to observe potential synergies.
- Longitudinal Studies: These trials monitor patients over time to identify long-term outcomes and effects of different management strategies. Observing the trajectory of NF1 can help in fine-tuning therapeutic applications.
- Patient Registry Studies: Collecting data systematically from NF1 patients can illuminate trends regarding treatment responses, disease progression, and quality of life impacts.
Potential Genetic Interventions
Looking ahead, genetic interventions present a tantalizing frontier. As our understanding of NF1 genetics improves, we’re better equipped to conceptualize therapeutic options that might one day be available:
- CRISPR-Cas9: This gene-editing framework has vast potential for addressing specific mutations in the NF1 gene. By precisely editing these genes, there’s a possibility to mitigate some of the disease's effects at the molecular level, a remarkable shift in how we approach genetic disorders.
- Gene Replacement Therapies: Future research might explore ways to replace faulty NF1 genes with healthy versions. Promising animal models and preliminary studies hint at possible methodologies that could transition into clinical practices.
- Personalized Medicine: As we continue to unravel the molecular heterogeneity of NF1, tailoring interventions based on individual genomic profiles may bolster treatment efficacy. Strategizing therapies according to a patient’s unique genetic makeup can revolutionize how medical practitioners handle the disorder.
These advancements in research underscore a collective leap towards comprehending NF1 more thoroughly and shaping the future of its management. As we stand on this precipice of change, stakeholders in the healthcare system must engage in ongoing collaboration, continually updating strategies in line with new findings.
Living with NF1
Living with Neurofibromatosis Type One (NF1) extends well beyond the medical aspects of diagnosis and treatment. It encompasses the emotional, psychological, and social dimensions that individuals and families must navigate daily. By shedding light on the realities faced by those with NF1, we can appreciate the holistic approach required for effective care and support.
Patient Perspectives
The experiences of individuals living with NF1 can vary greatly, making it crucial to listen to their stories. Some patients describe a challenging journey marked by uncertainty. The unpredictability of NF1 symptoms, such as tumor growth and skin changes, can lead to feelings of anxiety and distress.
Others find solace in community and shared experiences. They express gratitude for the understanding friends and family offer. Peer support becomes a lifeline. Engaging with others coping with similar issues fosters a sense of belonging. For many, sharing their journey serves not only as catharsis but also as empowerment—transforming personal challenges into advocacy for awareness and support.
Furthermore, the importance of education cannot be understated. Many patients emphasize the value of becoming informed about their condition, which in turn aids in self-advocacy. Understanding NF1 allows them to ask pertinent questions during medical appointments and seek tailored treatments.
Educational Support and Resources
Access to credible educational resources is essential for patients and their families. Knowledge about NF1 can ease fears and provide insight into what to expect. Organizations like the Neurofibromatosis Network and Children’s Tumor Foundation offer a wealth of information—from clinical guidelines to personal stories.
Additionally, educational materials should cover not just the medical, but also psychosocial aspects of life with NF1. Topics such as coping strategies, self-care, and navigating relationships are vital. Research indicates that comprehensive support contributes to improved quality of life for those affected.
Here are some key resources that can be helpful:
- Neurofibromatosis Network
- Children’s Tumor Foundation
- Educational forums on platforms like Reddit or Facebook offer communities for real-time support and dialogue.
Support Networks and Advocacy
Support networks play a significant role in the lives of those dealing with NF1. Advocacy organizations work tirelessly to promote awareness, fund research, and create community connections. They function as bridges between patients, families, and healthcare professionals, making sure that the unique needs of individuals with NF1 are highlighted and addressed.
On a local level, support groups offer a safe space to share experiences and resources. These meetups allow for face-to-face connections, fostering encouraging relationships that can diminish feelings of isolation. In major cities, various charities host events that unify the NF1 community, providing both fun and informative experiences.
Advocacy doesn’t stop at support and connection; it also extends to policy change. Many organizations are involved in lobbying for better healthcare provisions, funding for research, and increased public awareness campaigns. Patients often become ambassadors, sharing their stories to drive change and inform the public.
"Community is at the core of living with NF1. The more we share our stories, the stronger we become in facing our challenges."
"Community is at the core of living with NF1. The more we share our stories, the stronger we become in facing our challenges."
Finale
A well-rounded conclusion is not just a summary; it's a pivotal element that encapsulates the essence of any discourse. In the realm of Neurofibromatosis Type One (NF1), the conclusion serves several important functions that go beyond simply reiterating previously mentioned points. It urges a reflective understanding of NF1's complex interplay between genetic factors and clinical manifestations, spotlighting the necessity of nuanced approaches to diagnosis and management.
The key takeaway from this article is the multi-faceted nature of NF1 itself. It’s critical to grasp how this disorder uniquely affects individuals, manifesting not just as skin tumors but as a variety of systemic complications that can influence quality of life. The call to action here is for both medical practitioners and patients to recognize the significance of personalized management plans, which can significantly alter patient outcomes.
Furthermore, acknowledging the emotional and psychological impact this condition has on those who live with it is essential. The conclusion thus highlights the importance of integrating psychosocial support into treatment protocols, which is often the backbone of effective management strategies.
The implications of NF1 extend beyond individual patients to encompass broader public health considerations. Educators, researchers, and healthcare professionals must actively collaborate to foster a multi-disciplinary approach to NF1, capturing diverse insights to enrich ongoing research and provide comprehensive patient care.
In summation, the conclusion reinforces that the study of NF1 is not static; rather, it’s an ever-evolving field. Established knowledge lays the groundwork for further discoveries, emphasizing the pressing need for continued research and partnership in order to realize the full potential of therapeutic advancements.
"Unified efforts can carve out pathways to breakthroughs, shaping not only therapy but the very lives impacted by NF1."
"Unified efforts can carve out pathways to breakthroughs, shaping not only therapy but the very lives impacted by NF1."
Summary of Key Points
- Neurofibromatosis Type One (NF1) is more than just a genetic disorder; it is a complex interplay of various clinical manifestations, emphasizing a personalized approach to treatment.
- The need for multidisciplinary care is paramount, bridging medical, educational, and psychological realms for comprehensive health management.
- Ongoing research is essential for enhancing the understanding of NF1 and developing new therapeutic strategies.
- Patients living with NF1 face not only physical challenges but significant psychosocial implications, necessitating additional support systems.
Importance of Ongoing Research Efforts
Research into Neurofibromatosis Type One is not merely academic; it holds the potential to transform lives. As new studies emerge, they broaden the horizons of understanding regarding the genetic, environmental, and developmental nuances of NF1. Advances in this field can result in the following:
- Discovery of Novel Treatments: Research has the capability to discover and refine new therapeutic interventions that can alleviate the symptoms or slow the progression of NF1. This includes exploring gene therapies and targeted biologics that might one day transform the treatment landscape.
- Enhancing Screening Protocols: Understanding the unique manifestations of NF1 encourages the development of tailored screening protocols. This allows for earlier diagnosis and intervention, which is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes.
- Expanding Education and Awareness: Ongoing research increases public and professional awareness about NF1, creating a well-informed community that can advocate effectively for patient needs. This education can spur changes in healthcare policy that enhance the delivery of care.
- Fostering Collaboration: The complexities of NF1 require contributions from various fields. Ongoing research creates a platform for collaboration among geneticists, clinicians, psychologists, and educators, offering a holistic approach to this multifaceted condition.



